Journal of Nursing

Orthodox Jewish Medical Beliefs and Practices
his article provides an overview of Orthodox Jewish medical beliefs and practices. It emphasizes how the Orthodox faith influences healthcare decisions. The article explains key pracitices such as observance of the Sabbath, daily prayer routines, and strict modesty may affect patient care. Overall, this article stresses that healthcare providers should respect and accomadate Orthodox Jewish traditions and how their faith guides every decision.
Read More →
Impact of Stress and Lifestyle on Cardiac Health in College Students
This article explores how stress and lifestyle habits influence cardiac health in college students. It emphasizes the role of nurses in promoting heart-healthy practices and managing stress. Observations suggest that irregular meals, sedentary routines, and late-night study patterns increase cardiovascular risk.
Read More →
The Unmeasured Discomfort: Shivering in PACU and The Use of a Bedside Shivering Assessment Scale
Postoperative shivering is a common complication of general anesthesia. This can cause patient pain, distress, and hemodynamic changes. Nurses should use a BSAS to assess the severity of shivering and take appropriate interventions to minimize this with pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods.
Read More →
The House of the Least of These
This is a brief article about the impact of advocating for your patients in a correctional facility.
Read More →
Evidence Based Practice - Ultrasound Guided Peripheral IV Placement
This study aims to show that nurse driven placement of ultrasound guided peripheral intravenous access in the emergency department will improve patient care.
Read More →
Nurse Burnout: Am I the Only One?
A poetic piece on burnout in nursing with a positive note added.
Read More →
The Vagina :Bringing the Vagina Back to Life After Menopause Non-Hormonal Treatment Approaches for Atrophic Vaginitis and Chronic UTIs in Estrogen-Restricted Women In honor of the women who have suffered in silence
This paper is dedicated to the many women I have had the privilege of treating for atrophic vaginitis during menopause. Atrophic vaginitis—characterized by vaginal dryness, tissue thinning, and the involution of the vagina, labia, and urethra—is primarily caused by estrogen deficiency. I reflect on the voices of women whose needs have been unmet due to contraindications for estrogen therapy, often stemming from a history of cancer or other medical concerns. This work seeks to explore evidence-based, non-hormonal alternatives to manage atrophic vaginitis in menopausal women who cannot undergo estrogen therapy. Atrophic vaginitis does not affect the vagina alone—it also compromises the urethra, labia minora, labia majora, and the vaginal introitus (Faubion et al., 2017). Many of my patients have expressed frustration and distress as they navigate these symptoms without access to estrogen treatment. Their suffering and pleas for relief fuel the urgency of exploring and validating safe, effective, and estrogen-free therapeutic options.
Read More →
All the Hats We Wear: The Soul of a Nurse
This article explores the many roles that nurses take on- mentor, leader, advocate, caregiver- and highlights how the essence of nursing goes beyond clinical expertise to the heart of human connection. As new generations enter the profession in a post-COVID, increasingly virtual world, many lack opportunities to develop crucial interpersonal skills. The piece emphasizes the importance of mentorship, modeling compassion, and preserving the "old-school" art of nursing to ensure the soul of the profession endures.
Read More →
The Effect of A Neurological Training Module On The Competency of Neurocritical Care Staff Nurses
In this study, the competency training module had an effect in the post-test in the aspects of cognitive and affective domains only; thereby, accepting H1 and H0 was rejected. The training module did not affect the psychomotor domain. Based on the results of the study, H2 was accepted, there was no significant difference between the staff nurses’ profile with the results of the post-test; therefore, H3 was rejected. In this study, the competency training module had an effect in the post-test in the aspects of cognitive and affective domains only; thereby, accepting H1 and H0 was rejected. The training module did not affect the psychomotor domain.
Read More →
Silenced and Overlooked: The Impact of Societal Norms on Women’s Mental Health Care
This article examines the ongoing influence of societal norms and gender bias in the treatment of women’s mental health. Despite advances in medical understanding, many women continue to face dismissal, misdiagnosis, and emotional invalidation within clinical settings. Drawing on contemporary research and lived experiences, the paper sheds light on issues such as medical gaslighting and diagnostic overshadowing, emphasizing how these challenges impact trust, access, and outcomes. It calls for greater awareness among healthcare providers, particularly nurses, and advocates for a more compassionate, inclusive approach to mental health care that validates the experiences of all patients.
Read More →The Effect of A Neurological Training Module On The Competency of Neurocritical Care Staff Nurses
In this study, the competency training module had an effect in the post-test in the aspects of cognitive and affective domains only; thereby, accepting H1 and H0 was rejected. The training module did not affect the psychomotor domain. Based on the results of the study, H2 was accepted, there was no significant difference between the staff nurse's profile with the results of the post-test; therefore, H3 was rejected. In this study, the competency training module had an effect in the post-test in the aspects of cognitive and affective domains only; thereby, accepting H1 and H0 was rejected. The training module did not affect the psychomotor domain.
Read More →
A Retrospective on Nursing During the 2014 - 2016 Ebola Outbreak
The 2014-2016 Ebola virus disease (EVD) epidemic in West Africa was one of the most severe global health crises of the 21st century. Nurses, as the largest group of direct care providers, faced extraordinary risks and responsibilities during this outbreak. This document explores the multifaceted role of nurses in EVD management, emphasizing the dangers they faced, the leadership they provided, and the public’s shifting perception of their work. The document also addresses how Ebola’s transmission dynamics and containment measures affected nursing practice, and how the epidemic evolved into a complex humanitarian emergency (CHE). Through analysis of documented experiences, media coverage, and global responses. This document illustrates the essential contributions of nurses during the EVD crisis and underscores the need for better support and recognition of nursing roles in future epidemics.
Read More →
Colorectal Cancer in Younger Adults: A Growing Concern and a Call to Action
Colorectal Cancer in Young Adults, Early Detection Methods, Warning Signs to Look For
Read More →
More Than Evidence: How Experience and Reflection Shape My Epistemological Stance in Nursing
This paper explores the author's personal epistemological stance in nursing, emphasizing the integration of both empirical evidence and experiential knowledge gained through clinical practice. Drawing on Barbara Carper’s four patterns of knowing, empirical, personal, ethical, and aesthetic, the author highlights how meaningful nursing care requires more than scientific knowledge; it also demands relational understanding, critical reflection, and empathy. A fictional case study is used to illustrate how these ways of knowing intersect in real-life decision-making, particularly when caring for marginalized patients. The paper ultimately argues for a holistic, patient-centered approach to nursing that honours both objective data and the lived experiences of patients.
Read More →
Patient Autonomy
An article discussing honoring patient autonomy while maintaining professional obligations.
Read More →

From Classroom to Chaos: A Concept Paper on Transitional Dissonance in the Nursing Profession
This concept paper explores transitional dissonance experienced by newly licensed nurses as they move from academic training to clinical practice. It identifies key factors contributing to this dissonance, including the gap between theoretical preparation and real-world clinical demands, role ambiguity, inadequate organizational support, emotional labor, cultural challenges, and rapid technological changes. The paper highlights how these interconnected issues lead to stress, burnout, job dissatisfaction, and high turnover, ultimately impacting nurse well-being and patient care quality. Understanding the causes and effects of transitional dissonance is critical for developing targeted interventions that support nurses’ professional adjustment and improve healthcare outcomes.
Read More →
Rebuilding Community and Resilience: Establishing a Wellness Committee to Support Nurses' Mental Health Post-Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly exacerbated burnout and emotional distress among nurses, eroding workplace cohesion and well-being. Recognizing the limitations of existing mental health resources, one nursing unit established a wellness committee focused on fostering community, inclusivity, and mental health support. This article describes the committee’s initiatives—including social events, support during local Pride parades, care packages for new mothers, and promoting wellness tools—and highlights measurable outcomes. In just the first year, the unit’s survey revealed a 25% increase in staff reporting that their mental health was being addressed and a rise in staff feeling able to be their authentic selves. These findings emphasize how grassroots efforts can play a critical role in restoring resilience and connection among nurses, contributing to better retention, morale, and patient care outcomes.
Read More →
Addressing the Global Nurse Migration Crisis: Strategies for a Resilient and Equitable Healthcare Workforce
This article is about the global nurse migration crisis caused by disparities and instability, which worsens shortages in poorer countries. It proposes a framework of Protection, Equity, and Collaboration to address these issues ethically and sustainably. The approach supports the UN’s goals for equitable and resilient healthcare systems worldwide.
Read More →
Using Virtual Reality Simulation as a Tool to Improve Clinical Competencies
Simulation has long been recognized as an effective instructional method in nursing education. The use of virtual reality simulation as compared with traditional simulation, adds a new dimension to the complexity of simulated patient care. In this study, students’ perceptions of improved clinical competencies such as confidence, priority setting, delegation, time management, and communication were evaluated using a post simulation survey and reflective journaling. Results demonstrated an improvement in clinical competencies.
Read More →
Use of Structured Educational Programs Directed to Healthcare Providers to Improve Patients' Adherence to CKD Medications.
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) presents a significant public health challenge due to its progressive nature, associated comorbidities, and increasing prevalence in the United States. One of the critical barriers to effective CKD management is poor patient adherence to prescribed medication regimens. This Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) project aimed to assess the effectiveness of a structured educational program for healthcare providers in a South Florida medical center to improve medication adherence among CKD patients. Guided by Patricia Benner’s Novice to Expert Theory, the project utilized a pre-posttest quasi-experimental design to evaluate changes in provider knowledge and perceived confidence in managing medication adherence. The intervention included an evidence-based educational PowerPoint presentation targeting healthcare professionals—physicians, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, nurses, and medical assistants—who care for CKD patients. Participants (n = 21) completed a pretest to assess their baseline knowledge, attended the educational session, and then completed a posttest to evaluate the improvements. Data analysis showed a marked increase in posttest scores and self-reported confidence, with 81% of participants demonstrating enhanced understanding of CKD medication adherence strategies. Results support the efficacy of provider-directed educational programs in promoting adherence behaviors in CKD patients through improved communication, individualized care planning, and consistent follow-up. The project underscores the importance of providing education in addressing non-adherence medication and serves as a scalable model for other chronic disease management initiatives. Findings were disseminated to institutional stakeholders and prepared for publication to encourage broader implementation. Keywords: Chronic Kidney Disease, medication adherence, healthcare providers, educational intervention, DNP project, Patricia Benner, structured education, patient outcomes
Read More →
From Classroom to Community: Teaching Stress First Aid
This narrative describes an initiative to teach nursing students the Stress First Aid model to promote mental wellbeing and resilience in nurses. Students found the value in SFA, they taught older adults stress management skills they learned.
Read More →
The Challenges of a CVICU Nurse and The Toll of Burnout: The Bedside Nurse Perspective
The Cardiovascular Intensive Care Unit (CVICU) represents one of the most challenging healthcare positions due to the overall demand for exceptional clinical expertise, both in advanced clinical abilities and emotional resilience. CVICU nurses manage severe cardiac health crises while executing difficult medical interventions and making critical decisions during emotionally intense situations. Recent research shows that more than 40% of ICU nurses experience burnout, which leads to significant impacts on their personal lives and mental health, as well as patient care and outcomes. The article investigates the fundamental causes of burnout in CVICU nurses and its extensive impacts while providing actionable personal and organizational solutions to tackle this escalating problem. The elimination of burnout represents both a moral duty and the key to maintaining top-notch patient care and nurse retention.
Read More →
The Old Machine Shop
This story of The Old Machine Shop is one of the reasons why I am so dedicated to the field of Hospice Nursing.
Read More →
Cross-Cultural Nursing Leadership: A Comparative Reflection On Managing Healthcare Teams In The Philippines And Abroad
This reflective journal explores cross-cultural nursing leadership as experienced by Filipino nurses working in diverse healthcare systems—specifically in the Philippines, the United Kingdom (UK), the United States of America (USA), and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA). Drawing from our multifaceted roles as bedside nurses, educators, and administrators, we examine the interplay between cultural expectations, leadership styles, team dynamics, and systemic structures. This reflection identifies common values, contextual differences, and lessons that can be applied to shape resilient and culturally responsive nursing leadership education in the Philippines. Through critical introspection grounded in personal and collective experiences, this journal aims to contribute to the cultivation of globally competent, ethical, and adaptable Filipino nurse leaders.
Read More →
Nurse Burnout: Am I The Only One?
A narrative style piece commenting on burnout in the nursing profession
Read More →
Community Service: Undergraduate Nursing Students Perspectives on Participating in a RAM Clinic
An article on the experience that senior nursing students experienced while engaging in the Remote Area Medical (RAM) clinic. The senior nursing students were able to utilize their various skills, including nursing care, assessment, communication, education, and clinical judgment. The ability to interact and function as a nursing student enhanced their self-confidence and strengthened their perception of the significance of real-world community service.
Read More →
Emergency Room Nurses Gave Gunshot Victim’s Drugs To Police: No Violation of Patient’s Rights.
The emergency room nurses were not working for the police, but were following hospital protocols for gunshot victims in the E.R.
Read More →
Finding Purpose in Survival: A Second Chance to Inspire Others
Sean faced heart, kidney, and respiratory failure at 55—but survived against all odds and found his purpose in nursing. His story is one of resilience, gratitude, and second chances.
Read More →
How Concept Maps Facilitate Learning in Nursing Education
Concept maps are visual tools that help nursing students organize and connect complex information. They promote critical thinking by encouraging analysis and synthesis rather than rote memorization. In both classroom and clinical settings, concept maps support deeper understanding and better care planning. They also enhance collaboration and peer learning. Overall, concept maps strengthen cognitive skills essential for effective nursing practice.
Read More →
Enhancing Inpatient Care Through Interprofessional Collaboration: The Nurse's Impact
This essay explores the pivotal role of nurses within the context of interprofessional education (IPE) and interprofessional collaborative practice (IPCP) in hospital settings. It emphasizes the importance of effective teamwork in dynamic, high-pressure environments and highlights the Camden Coalition's healthcare hotspotting initiative, which provides comprehensive care to high-cost, high-needs patients through interprofessional teams. The identifies key vulnerable populations that “may fall through the cracks”, such as justice-involved or homeless individuals, and underscores the essential role of nurses in identifying and coordinating care for them. It also calls for more robust research to examine the links between nurse-driven IPE and patient-reported experience measures, focusing on patient safety indicators and team efficiency metrics.
Read More →Healthcare Reimagined: The Transformative Impact of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing diagnostics, personalizing treatment plans, and optimizing hospital operations. It empowers medical professionals with tools for early detection of diseases, predictive analytics, and robotic-assisted surgeries. AI-driven innovations are also improving patient experiences through virtual health assistants, streamlined administrative processes, and telemedicine advancements. While challenges such as ethical concerns and data privacy remain, the ongoing integration of AI promises to reshape healthcare into a more efficient, accurate, and patient-centered industry.
Read More →
Maternal Mortality Among Black Mothers in Massachusetts
This is an op-ed about the need for further attention and funding to combat the rising rates of maternal mortality of Black and Haitian mothers in Massachusetts.
Read More →
Revolutionizing Nursing Education: The Impact of Virtual Reality and Simulation Technologies
The rapid evolution of virtual reality (VR) and simulation technologies is transforming nursing education by enhancing clinical training, improving decision-making skills, and fostering experiential learning. These advanced tools provide immersive and interactive environments that simulate real-world clinical scenarios, allowing nursing students to develop critical competencies in a safe and controlled setting. This paper examines the integration of VR and simulation technologies in nursing education, focusing on their impact on clinical skill acquisition, critical thinking, and patient safety. Additionally, it addresses the challenges of adopting these technologies, including cost, accessibility, and the need for faculty training. By exploring current innovations and future directions, this paper highlights the transformative potential of VR and simulation in preparing future nurses for complex healthcare environments.
Read More →
Empathy vs. Emotional Reasoning -What is the Difference?
It is mind reading when one person proposes to know what another person is thinking or feeling. Emotional reasoning is defined as "a cognitive error whereby a person who is nervous or anxious resorts to emotional reactions to determine a course of action. Nurses need to be aware of this in treating patients.
Read More →
Rolling Away
This heartfelt article recounts a humorous yet poignant moment at a long-term care resident council meeting, where a lighthearted suggestion about putting weed in breakfast muffins sparks laughter and deeper reflections on autonomy. Through the lens of an Ombudsman, it highlights the importance of listening not just to complaints, but to the joy, imagination, and desire for choice that still thrive in residents' lives.
Read More →
Prolonged Grief, Loneliness and Depression
A groundbreaking study explores how prolonged grief symptoms contribute to loneliness and depression, shaping mental health interventions.
Read More →
Innovation and Technology in the AI Era: Enhancing Healthcare Systems and Nursing Care in the U.S.
This paper explores the impact of AI innovations in the U.S. healthcare system, particularly within the nursing profession. Key AI applications such as predictive analytics, robotic assistance, personalized medicine, and virtual nursing assistants are examined.
Read More →
The Power of Word Choice in Healthcare Settings: A Critical Examination
Effective communication is vital for high-quality patient care in healthcare settings. Both verbal and non-verbal communication significantly impact patient outcomes and experiences, especially for cognitively impaired individuals. Miscommunication can lead to distress and misunderstandings. This article explores the nuances of verbal and non-verbal interactions, offering real-life examples of miscommunication and practical strategies for healthcare providers. By prioritizing clarity, empathy, and cultural sensitivity, healthcare providers can foster trust, reduce anxiety, and improve overall patient care.
Read More →
Advocating for the Vulnerable: Upholding Core Values in Healthcare and Education
In both healthcare and education, true leadership embodies service over self-interest, building bridges instead of walls, and leading with integrity. Advocates in these fields play a crucial role in ensuring that individuals' voices, wishes, and preferences are heard, their rights are upheld, and their needs are met, particularly when they have difficulty speaking up for themselves.
Read More →
The Negative Impacts of Fast-Track Nursing During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Fast-tracked nursing graduates faced challenges due to limited training during COVID-19. Learn how this impacted patient safety, workplace dynamics, and the future of healthcare.
Read More →
Emma: raised in a care facility
I have been working closely with a little girl who has spent her life in a long-term acute care facility, and I am heartbroken by her lonely existence.
Read More →
Hypertension Patient Education
A lesson plan for hypertension in the cardiology clinic setting.
Read More →
The Crucial Role of DEI in Education and Healthcare
The U.S. population is becoming increasingly diverse. This demographic shift underscores the urgent need for culturally and linguistically competent healthcare professionals and educators from diverse backgrounds. Incorporating DEI education becomes vital for preparing a workforce equipped to improve health outcomes for the communities they serve.
Read More →
The Importance Of The Nurse Role In A Turner Syndrome Multidisciplinary Clinic
The Turner Syndrome Multi-Disciplinary Clinic (TSMDC) was established in 2015 to provide comprehensive, coordinated care for TS patients and their families. Initially led by a genetic counselor, the clinic evolved with a nurse coordinator taking over in 2018, streamlining patient triage and care coordination. The nurse coordinator ensures seamless communication between providers, organizes necessary tests, and helps maintain adherence to clinical guidelines. Over the years, the clinic expanded its team and services, leading to increased patient accessibility and improved outcomes. With a 90% adherence rate to clinical guidelines, TSMDC highlights the crucial role of nurse coordinators in enhancing efficiency, patient care, and long-term well-being.
Read More →
Enhancing Nursing Education: Unfolding Case Studies with Standardized Patients for Difficult Conversations
Discussing the use of standardized patients (SPs) for difficult conversations with patients regarding substance use. We included student feedback to support the importance of using SPs.
Read More →
Celebration Party
Hi I had to write a "celebration party" paper at the end of my first semester in school when i was in school for my MSN. I always held on to this paper because even though it didn't need references, it was just a story from ourselves. I thought one day I would try to publish it if possible. I reached out to my professor at the time who said it would be ok to use her real name in it. I will post it below.
Read More →
The Future of Healthcare Training: Embracing Online Learning Platforms
The healthcare industry is ever-evolving, and with it, the methods of educating and training future professionals are also transforming. Online learning platforms have emerged as a game-changer in healthcare education, providing students and professionals with the tools to gain knowledge and skills in flexible and accessible ways. This shift is not just a response to modern technology but also a reflection of the growing need to meet the demands of a dynamic and complex healthcare landscape.
Read More →
Addressing the Nursing Shortage
The nursing shortage, a critical issue in the U.S. and globally, is driven by interconnected factors and projected to persist for years. Addressing this challenge requires innovative educational programs, expanded partnerships, and systemic solutions to build a sustainable nursing workforce.
Read More →
How to Stay Current with Continuing Education in Nursing
Continuing education empowers nurses to stay current, advance their careers, and provide high-quality patient care in an evolving healthcare landscape.
Read More →
Top Trends in Healthcare Technology That Are Changing Patient Care
A look into the top cutting-edge technologies revolutionizing healthcare, from AI-driven diagnostics to telemedicine and wearable tech, transforming patient care and medical efficiency.
Read More →
Breaking Barriers: Addressing Transportation Challenges and Healthcare Access for Expectant Mothers in Impoverished Communities
Access to healthcare is a critical component of health equity, yet impoverished and rural communities face significant barriers, particularly due to a lack of reliable transportation. This work explores how transportation challenges disproportionately affect access to prenatal care for pregnant women, contributing to adverse maternal and neonatal health outcomes.
Read More →
The Elusive Lessons of Encephalitis Lethargica
Encephalitis Lethargica (EL) emerged as a deadly pandemic in the early 20th century, leaving many permanently disabled. Though rare today, its cause remains unknown. EL has two forms—dyskinetic (children) and Parkinsonian (adults). Researchers suspect links to influenza and COVID-19 due to shared neurological effects. Treatment is limited, and future viral pandemics could trigger EL’s return.
Read More →
An Effective Orientation Program is Key to Laying the Framework within a Virtual Nursing Environment
This article describes the importance of developing a well-structured orientation for virtual nurses. It also outlines components to include in a virtual nursing orientation.
Read More →
The Preconception Blueprint: What Women Need to Know Before Trying to Conceive
The journey of motherhood begins long before pregnancy is confirmed, with preconception health playing a pivotal role in both maternal and fetal well-being. The preconception period is technically defined as the three months prior to conception, because that is typically the amount of time it takes for a fertile couple to conceive (Stephenson et al.). This paper explores the essential components of preconception planning including nutritional considerations, lifestyle modifications, environmental factors, and psychological readiness. Nutritional health is critical, as deficiencies in the body can negatively affect fertility and fetal development. Certain lifestyle choices such as being physically active and refraining from smoking plays a large part in enhancing reproductive health. In addition, environmental toxins and pollutants must be assessed to minimize risks during conception and pregnancy. Furthermore, psychological readiness is vital for coping with the challenges of pregnancy and parenting. All in all, a comprehensive understanding of preconception health can empower women to make informed decisions and enhance their journey through pregnancy.
Read More →
Critical Care Chronicles
Utilizing a journal for Intensive Care Unit patients to help manage the day to day challenges, physically and emotionally during their stay. Along for emotional release, better communication, or recollection of the events that took place.
Read More →
Introducing De-escalation Techniques in Nursing Education
Introduces the need to address the potential to encounter violence in the workplace and how de-escalation and physical crisis intervention can be utilized to promote safety for the patient and the staff members. It includes the importance of utilizing the team approach and staff debriefing after a physical intervention.
Read More →
Saving Flatlines Through Mechanical Resuscitation
Introducing the new Lucas device, which provides mechanical resuscitation, allowing for better patient outcomes during a cardiac arrest.
Read More →
A Nursing Approach to the Efficacy of Corticosteroids in Community Acquired Pneumonia Treatment
This study aims to describe the use of corticosteroid therapy in treating community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), determine differences in morbidity and mortality between groups receiving corticosteroids and groups receiving standard care, and examine relationships among clinical outcomes. This literature review will explain and determine the effect of corticosteroids on patient recovery and assess the efficacy and safety of corticosteroids in CAP treatment.
Read More →
To the Nursing Students...
The article is directed to nursing students who have maybe lost hope during nursing school and to let them know that there is a happy ending to their journey. I was one of those people who struggled greatly, but came out stronger with my dream job. It is important for nursing students to hear that it does get better.
Read More →
My Experience as a Stroke Nurse
As a stroke nurse, the role involves providing high-quality clinical care and offering emotional support to patients and families during challenging times. Stroke care requires medical expertise, empathy, and critical thinking. Nurses assess neurological function, administer medications, and work closely with a multidisciplinary team to ensure comprehensive recovery. The rehabilitation phase involves guiding patients through recovery while addressing their physical, emotional, and psychological needs. Nurses also educate patients and families on stroke prevention and lifestyle changes. The role is deeply rewarding as it allows nurses to help patients regain independence and improve their quality of life while continuously learning and advocating for stroke awareness and prevention.
Read More →
Professionalism in Nursing: Presenting Yourself as a Professional
Professionalism in nursing is often defined as acting with altruism, caring, and professionalism. Professionalism is defined as the educational level required to enter the field. Presenting yourself as a nursing professional depends on several other factors, including your resume/CV, professional attire, social media accounts, and participation in professional organizations.
Read More →
Compassion in Care: Rethinking Pain Management for Patients with Opioid Use Disorder
Op-Ed discussing post-operative pain management options for patients with Opioid Use Disorder. Every patient deserves adequate pain control, no matter their personal or medical history. Ensuring adequate pain control for all patients is a fundamental aspect of compassionate, effective healthcare, but it is especially crucial for patients with OUD. A carefully designed, multimodal protocol that reduces opioid use but still provides relief allows patients with OUD to recover safely and with dignity. This, in turn, lowers their risk of dependency complications while supporting both their physical and psychological healing.
Read More →
Capnography: A Missed Vital Sign in Post Anesthesia Care Units
Capnography provides essential data on how well a patient is ventilating regardless of what the oxygen saturation monitor is reading. This is an under-utilized tool that can detect adverse respiratory events such as hypoventilation leading to hypoxia. Capnography is a non-invasive nasal cannula that sits just below the nose and captures end-tidal carbon dioxide. Nurses should make it a standard of practice to implement capnography for all patients who arrive into the PACU.
Read More →
Sending nursing home residents with dementia to inpatient psychiatric units - Improvement or Retrogression?
Looks at the overuse of sending residents of longterm care settings with dementis to inpatient psychiatric units and the impact
Read More →
Punding - What is it?
Punding is a repetitive, purposeless behavior linked to excessive dopamine activity, often seen in Parkinson’s disease and stimulant use. It involves obsessive handling or assembling objects and is treated by reducing dopamine-enhancing drugs or using alternative medications.
Read More →
Embracing the Climb: From Cleaning Floors to a DNP
From mopping floors to earning a Doctorate in Nursing Practice, this powerful story showcases the resilience, determination, and passion that turned a nursing assistant into a healthcare leader.
Read More →
The CMO Curtain (A Poem)
I am submitting my poem for publication which highlights the importance of nursing care for patients at end of life. I am often disheartened when I hear other nurses dismissing care to a patient because they have chosen comfort measures only, CMO. I have been a nurse for 15 years and have specialized in hospice and palliative care since 2012. I became certified in the specialty in 2015. I am passionate about educating nurses, providers, and other caregivers on providing dignified end of life care. I look forward to hearing from you! Sincerely, Jennifer Carolan
Read More →
The Effect of an Integrated Mobile Smart app on the Reduction of Patient Readmission Rate
Demonstrate that managing patient's health by integrating a smart mobile app with an existing electronic health records system can reduce incidents of disease recurrence or relapse among discharged patients.
Read More →
The Role of Rhythmic Breathing in Stress Reduction for Clinical Nurses
Nursing workload has dramatically changed over the last twenty years. The job duties of acute care hospital medical surgical nurses have changed and has contributed to a shift in nursing well-being and overall work-related stress. A descriptive cross-sectional study was performed to teach acute care medical surgical nurses pranayama/rhythmic breathing to reduce stress and improve well-being. Well-being and stress surveys were collected pre and post intervention. The results of the surveys indicated the training with daily reminders for rhythmic breathing improved, as evidenced by improvements in World Health Organization- 5 Well-being index scores (WHO-5), while the stress surveys did not reveal significant changes. The results of this descriptive cross-sectional study revealed the simple intervention of teaching medical-surgical nurses rhythmic breathing has the potential to improve their overall well-being.
Read More →
The little moments that help keep nurses going
Recounting an incredible experience as a NICU nurse that helps keep me motivated to stay in the field.
Read More →
The Challenge Of Choosing Your Practice Area As An Early Career Nurse
After graduating with a Bachelor of Science in Nursing, you have completed the qualifications to work in a variety of hospital and clinical settings, supporting patients' needs and further advancing your own practical education. As registered nurses (BScN), we never stop learning, as each patient brings unique challenges and opportunities to advance our skills. However, many struggle to decide where they want to hone their skills and what field they are truly passionate about, even after completing their early training.
Read More →
When will we stop tolerating violence against nurses
A discussion about workplace violence against nurses and the lack of polices and protection in place to protect the frontline workers at the bedside.
Read More →
Imaginary Audience / Personal Fable - Just a Phase or More?
Presents the question: Is the imaginary audience/ personal fable stage of development a hypothetical concept, a normal stage of development, a mental disorder, or a precursor of mental health disorders that may come in early adulthood?
Read More →
Exploring Diverse Career Paths in Pharmacy: Opportunities Await for Aspiring Pharmacists
Becoming a pharmacist means embarking on a rewarding journey in a field that offers a plethora of career opportunities. Pharmacy is far more than dispensing medications - it’s a dynamic and diverse profession with countless paths you can explore. Whether you’re drawn to patient care, research, or the corporate world, there’s a place for you. Let’s dive into the different career opportunities available to pharmacists and how you can find your niche.
Read More →
The Role of Technology in Modern Nursing: Transforming Patient Care
The healthcare landscape is rapidly evolving, and technology plays a pivotal role in this transformation. For nurses, integrating technology into their practice has become essential in providing efficient, high-quality care. This article explores the role of technology in modern nursing, highlighting the benefits, challenges, and future trends in this dynamic field.
Read More →
The Importance of Networking in Nursing School
Embarking on the journey to become a nurse is both exciting and challenging. While academic excellence and clinical skills are crucial components of nursing education, there is another vital aspect that often doesn't get as much attention: networking. Building a robust professional network during nursing school can significantly enhance your career prospects and provide invaluable support throughout your nursing journey. This article delves into why networking is essential for aspiring nurses and how to effectively build and maintain your professional connections.
Read More →
"Staying Prayed Up": A Poem
The basis of the poem originated from my dissertation titled: The Lived Experiences of Nursing Students Spiritual Well-Being During The COVID-19 Pandemic: A Phenomenological Research Study. The plethora of negative experiences was aggravated by experiences of social isolation arising from movement restrictions and social distancing requirements put in place as measures for containing the spread of the COVID-19 virus. The qualitative study aimed to examine the concept of the spiritual well-being of senior-level nursing students during the COVID-19 pandemic. Subsequently, the potential role of spiritual well-being in helping nursing students manage the stress associated with nursing school and coping during the pandemic. As the participants described religious practices being used as coping mechanisms the researcher was led to create the theme indicating a strong relationship with God thus, identified as a “Personal Relationship and Belief in God”. Mainly participants described spiritual well-being in the form of prayer, meditation, scripture, gospel music, apps of positive affirmation, and fasting. The descriptions of religious practices as coping mechanisms further provide insight into how spiritual well-being affects students’ ability to endure all of the hardships and survive during the COVID-19 pandemic. It seemed that no matter the circumstances that were endured the participant made a statement to confirm their faith. Many of the participants described their experience during the COVID-19 pandemic as relying heavily on prayer and staying “prayed up” to handle their experiences, therefore inspiring the poem “Staying Prayed Up”.
Read More →
Transitioning to Nursing: Making the Leap from One Career to Another
Switching careers can be a daunting but incredibly rewarding decision, especially when moving into the field of nursing. Whether you're coming from a completely different profession or a related field, the transition to nursing requires careful planning, dedication, and a passion for helping others. This article explores the challenges and rewards of leaving one career to pursue nursing and offers practical advice to help you navigate this significant change.
Read More →
Navigating Autoimmune Diseases: A Nurse's Personal and Professional Journey
This article highlights the importance of self-care for healthcare professionals, particularly nurses, and explores alternative career paths beyond bedside nursing. It is based on my personal journey with autoimmune diseases, including ankylosing spondylitis, Hashimoto's disease, and warm autoimmune hemolytic anemia. By sharing my story, I aim to educate on autoimmune diseases, encourage nurses to prioritize their health, and illustrate diverse nursing career opportunities.
Read More →
Finding the Right Nursing School: Aligning Your Values with Your Education
Choosing the right nursing school is one of the most crucial decisions aspiring nurses will make on their journey to an impactful career. While factors like accreditation, location, and cost are undoubtedly important, there's another critical aspect that often goes overlooked: alignment of values. This article explores why finding a nursing school that resonates with your personal and professional values is essential and how it can shape your future in healthcare.
Read More →
Integrating Large Language Models and Artificial Intelligence in Nursing Education
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the medical industry has brought about changes in patient care, diagnosis, and therapy. At the same time, higher education has realized that it needs to adapt to these technological advancements to ensure that future nurses have the knowledge and skills required in the rapidly evolving healthcare environment. This brief commentary aims to ascertain the implicit support that academic faculty members offer for the application of large language models and artificial intelligence in the teaching of nursing sciences.
Read More →
The Career Path of a Family Nurse Practitioner: A Journey of Care and Compassion
The role of a Family Nurse Practitioner (FNP) is both dynamic and rewarding, offering a unique blend of expertise and care. As healthcare continues to evolve, FNPs play a crucial role in providing comprehensive primary care to individuals and families across the lifespan. This article explores the career path of a Family Nurse Practitioner, outlining the educational requirements, job responsibilities, and potential career opportunities.
Read More →
Advocacy in Nursing Practice: Let's Promote it More
I decided to write an article around advocacy just to remind people how important it is.
Read More →Assessing Clinical Outcomes at Discharge with the Modified Rankin Scale (mRS) for Burn Patients
Burn injury is a significant health problem that presents various challenges to the patient and healthcare providers. Each year in the United States, an estimated 486,000 burn injuries require medical attention, of which 40,000 require hospitalization (American Burn Association, 2016). Of these 40,000 around 30,000 are admitted to specialized burn centers, specializing in burn care and management. Statistics reveal that the common causes of burns are due to fire/flame at 43%, scalds 34%, contact 9%, electrical 4%, chemical 3%, and other 7%. (American Burn Association, 2016). The most common place of occurrence was in the home at 73%. Burns occur in children and adults, affecting 68% of males and 32% of females. Also reported by the American Burn Association (ABA) was a survival rate for all cases at 96.8% (2016). Furthermore, a reported survival rate of 96.8% for all cases by the ABA (2016), underscores the importance of comprehensive care for burn patients, which begins at the time of injury and extends throughout the rehabilitation process. An optimal outcome is achieved when the patient is reintegrated back into society at a functional preinjury level (Herndon, D. 2017).
Read More →
Navigating Resource Challenges in Nursing Education: Perspectives from a Dean of a Nursing Program
By investing in nursing faculty, colleges and universities can increase the number of well-trained nurses entering the workforce, thus helping to address this critical shortage. However, it is a common sentiment among nursing faculty at colleges and universities that their counterparts in other disciplines may not fully appreciate the rationale behind the seemingly greater need for resources, including financial compensation, within nursing education. As a Dean of a Nursing Program, I share this frustration and exhaustion stemming from the continual effort required to justify why nursing faculty necessitate higher salaries and greater resource allocation compared to many other departments within the institution. Overall, the multifaceted nature of nursing education more often contributes to a higher workload for nursing faculty compared to their counterparts in other academic disciplines. Nursing education is multifaceted, a fact that many other disciplines do not fully understand.
Read More →
Navigating Nursing School: Do's and Don'ts for Aspiring Nurses
So, you’ve set your sights on becoming a nurse, congratulations! Nursing is a noble profession, full of rewards and challenges. But how do you make the most of your time in nursing school? What should you do, and what should you avoid? Let’s explore the essential do's and don’ts that will help you navigate nursing school successfully.
Read More →
Nurse Camp: Planting Nursing Seeds in High School
The nursing profession is challenged by a shortage of nurses and limited perceptions of nursing to meet the current health care demands. A summer Nurse Camp for todays youth may be one answer for more nurses tomorrow. Nurse Camp was created for high school students to explore the intricacies of the nursing profession, increase factual media exposure, and stimulate diverse interests in the nursing profession.
Read More →
My Journey With Asplenia...So Far
Essay on my personal experience as a nurse and a patient, in the sense of asplenia as my status now in life. Disclosure of my personal observations as an asplenic person whom is also a nurse.
Read More →
Clinical Depression vs. Layman's' Depression: What Nurses Need to Know
The general term depressed used by laymen doesn't match the medical definition used by Nursing. How to distinguish the two.
Read More →
Perspective Triad: The Role of the Nurse Informaticist in Higher Education
This article provides an analysis of how the role of the nurse informaticist can expand beyond the bedside and clinical nursing into higher education. Specifically, nurse informaticists can be beneficial to pre-licensure nursing programs as they can provide a three-fold perspective of nursing, informatics, and business to assist leadership to enhance student and programmatic outcomes.
Read More →
Take A Minute to Listen, It Could Save a Life
Listening for a carotid bruit might help save a life. Stroke cases are increasing and are debilitating to patients and their families. Listening to the carotids for one minute each time you listen to the heart since a 2mm carotid luminal narrowing can cause a bruit. If a bruit is detected, report this finding to the primary care provider to help curb the upward trend of strokes.
Read More →
The Impact Of Implementing A Patient-Centered Medical Home Model In The Primary Care Setting
Literature demonstrates a trend of shared decision-making models that are centered around the patient. By implementing the Patient Centered Medical Home (PCMH) model, patient encounters will encompass a patient-centered decision-making approach regardless of the reason for the visit. This model incorporates ongoing preventative screenings into routine visits to create a continuum of meeting wellness initiatives without relying on a routine wellness visit yearly. To implement this model, the clinician will thoroughly review the patient’s chart prior to the office visit. If any preventive screening is identified, then the primary care provider addresses the initiatives during the encounter. Post-implementation data showed a marked increase in ordered preventive screenings, wellness exams, and revenue to the clinic. There was also an increase in patient satisfaction perception among participating providers. The PCMH model allows the clinician avenues to address, create dialogue, and implement shared decision-making to incorporate preventative screenings and keep preventive care moving forward.
Read More →
The Role of the Forensic Nurse Examiner at the U.S.-Mexico Border
This article gives context to the migrant crisis at the U.S. border and describes gender-based violence and the role of the forensic nurse examiner in providing care for these victims of violence.
Read More →
Resuscitation for Cardiac Arrest Should Begin and End with Basic Life Support
The article discusses Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS), which includes medical interventions for cardiac arrest and cardiovascular emergencies beyond Basic Life Support (BLS). While ACLS utilizes interventions like epinephrine administration, oxygen usage, and advanced airways, the author argues that ACLS, particularly the use of epinephrine, fails to show significant benefits in terms of neurological recovery for patients and suggests that financial motivations might contribute to its continued use.
Read More →
The SSRI debate -Some thoughts
The article takes a look at the the debate over whether depression is caused by reduced serotonin or a combination of other factors.
Read More →
Crohn's Disease
The paper includes the identification, etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of Crohn's disease. The paper also addresses nutrition, diet, and nursing interventions and education to help manage the disease.
Read More →
The Secret Society of Mayhem and Abuse
The article highlights the crisis in global healthcare systems, particularly focusing on the immense stress on nurses. The author emphasizes that these challenges existed before the COVID-19 pandemic, with the crisis merely spotlighting them. Using personal anecdotes, they depict the struggles of nurses facing overwhelming workloads and unsupportive management. The article critiques the wage and responsibility disparity between nurses and hospital administrators, framing healthcare's issues as financial greed overshadowing patient care. The author calls on nurses to advocate for patients, emphasizing the need for unity and prioritizing care over financial motives.
Read More →
Conflicts between Sound Educational Practices and Meeting the Needs of Practice for a nursing Graduate in the era of COVID-19
The U.S. healthcare landscape is continually changing due to population diversity, technological advancements, and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, resulting in unique healthcare needs within multicultural communities. This evolution mandates nursing graduates to possess comprehensive skills to function in this dynamic environment. However, challenges such as full curricula, limited computer skills among nursing students, language barriers, and financial issues create a conflict between educational practices and practical requirements for nursing graduates. This article explores essential educational practices, highlighting the need for nursing programs to produce culturally competent graduates skilled in technology. It advocates for the incorporation of innovative learning strategies and curriculum flexibility in nursing education to foster sound educational practices, enabling graduates to meet the necessary outcomes and competencies in today's complex healthcare environment.
Read More →
Unwitnessed Falls in the Nursing Home: Finding the root cause
Understanding how effective post and pre-fall documentation can impact root cause analysis for unwitnessed falls in senior care settings
Read More →
Obesity Control Nurse Specialist
Obesity is a complex state described by excessive body fat. It is an ailment that increases the risk of emerging severe illnesses like heart and metabolic disease. According to WHO report 2020, approximately 2000 million adults are overweight and 500 million are obese worldwide, comprising 11 % men and 15 % women, or more than half a billion. Overweight and obesity have increased dramatically in the last 40 years. Obesity can easily be managed by choosing a healthy meal, more regular exercise, and controlling oneself.
Read More →
Nurses' Role in Promoting Food Safety Practices
Every year, nearly one out of every ten persons in the world has a foodborne illness, with 420,000 people dying as a result. Foodborne sickness, also known as "food poisoning," is caused when disease-causing germs or pathogens contaminate food. Vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort as well as fever, headache, and body soreness – are common indications of foodborne illness. Some kitchen-based measures that a nurse can promote to reduce the prevalence of food-borne illnesses are by organizing awareness campaigns in the community.
Read More →
The role of Sunlight, Vitamin D and nature in aiding cognition in mental health
Studies have found that low levels of Vitamin D leads to slower information processing, cognitive decline, mood disorders, and altered brain development and functioning that leads to medical issues and neuro-degenerative disorders.(1) When the patients of yesteryear were kept inside we were unwittingly worsening their mental health. How can we now aid our mental and cognitive health by using sunlight and food based Vitamin D?
Read More →
Empowered approaches for Type 1 Diabetes patient care in Canada
Diabetes diagnoses have skyrocketed in Canada the last two decades. Diabetes Canada released updated numbers in 2022 showing that 11.7 Million Canadians are living with Diabetes or PreDiabetes. These numbers are trending upwards with no sign of leveling off. Right now, more than $50 million dollars is spent every day on health care to treat diabetes and related complications.
Read More →
My Teaching Philosophy
It is imperative in nursing education to develop a teaching philosophy that presents the perspective of educators about learning, teaching, the learning environment, and clinical teaching, which is at the heart of nursing education.
Read More →
Racism, Implicit Bias, and Theory Failure in Nursing: How Cultural Competence Cloaks and Perpetuates Systemic Racism, Yielding Room for Improvement in Patient Outcomes and in the Profession
This article discusses how cultural competence and diversity impact nursing, highlighting the continued lack of equity in research, patient outcomes, and the profession itself. It argues that the Theory of Culture Care Diversity and Universality, developed over 30 years ago to promote cultural awareness in nursing, is outdated and fails to address issues of racism, systemic racism, marginalization, and inherent bias. The author calls for nursing theory to evolve and address these issues head-on, and for the voices and experiences of minorities and marginalized groups to be incorporated into nursing education and research to promote equitable care for all.
Read More →
Addressing the Effects of the Inadequacy of Prenatal and Postnatal Care Among Unhoused Women in Canada
This paper is a literature review that examines the effects of inadequate pre and postnatal and maternal care among unhoused women in Canada. It identifies the main health concerns and their implications on population health, explores health promotion and population empowerment strategies, as well as solutions for this issue and its implications on nursing practice.
Read More →
Positive Psychology in psychiatric and mental health nursing practice
Traditionally psychiatric practice has focused on treating mental illness and what is wrong with people. Treating the symptoms of mental illness can vastly improve quality of life and functioning but the absence of a mental illness does not guarantee a life of well-being or happiness. The billable codes of the DSM-5 are utilized to identify mental illness. It does not have a code or the listing of values for the symptoms or strengths in flourishing or a well meaning life. To combat this issue positive psychology and psychiatry has addressed this issue.
Read More →
Nurse Burnout: A Profession in Crisis
The COVID pandemic created the perfect storm with nurses retiring early and even quitting due to the overwhelming stress caused by the pandemic. A Nurse Manager, two staff nurses and a new nursing graduate working in the acute care hospital setting shared their view of why they think nurses are deciding to leave their current nursing jobs. Sadly most nurses reading this article, will likely relate to the stories that have contributed to nurse burnout and why nurses are leaving the profession and why we as a profession find ourselves in a critical crisis.
Read More →
Nurse "I am in Pain"
Pain education and management is important. Everyone suffers from pain at one point. Pain is very subjective and everyone should know when to seek help by medical professionals.
Read More →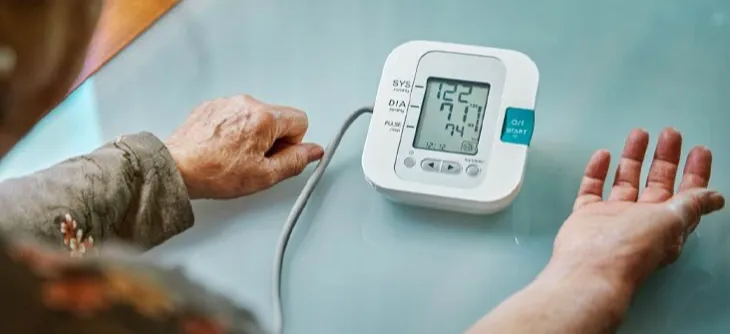
A nursing-driven approach towards reducing hypertension: a focus on evening dosing and circadian rhythm
There are increasing data supporting evening administration as a means of achieving better BP control through re-establishing normal sleeping dipping patterns, thereby preventing the development of comorbidities. Additionally, this dosing change has been shown to prevent the morning surge, a precursor to negative cardiovascular (CV) events, including heart attack and stroke. When the costs are high both fiscally and medically, simple and cost-free interventions should be the first-line treatments.
Read More →
Opposite of Burnout is Engagement
Facing a pandemic brought many nurses to a feeling of burnout, while this nurse was brought to engagement.
Read More →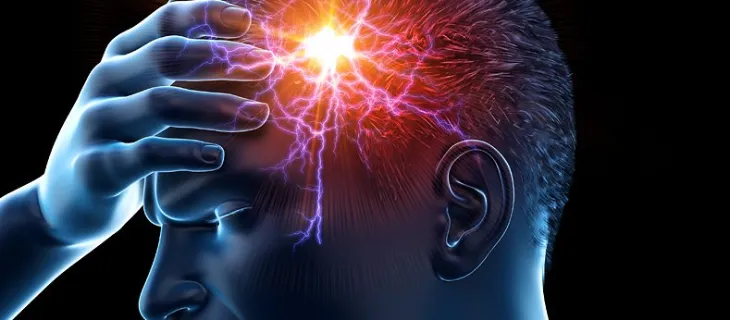
Migraine verses Bell's Palsy: A Case Study
Understanding the difference between migraine headaches and Bell’s Palsy will help drive appropriate care and treatment options for improved outcomes and a more rapid recovery.
Read More →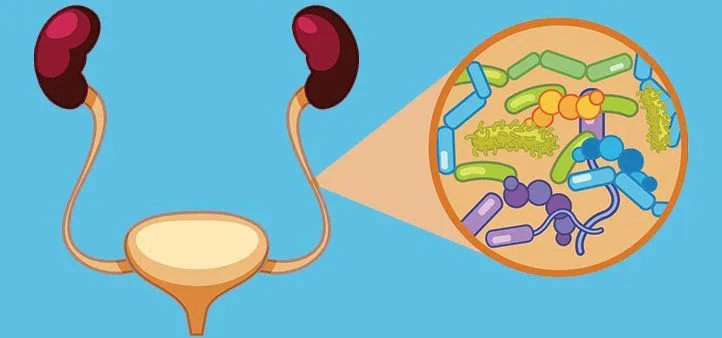
Pyelonephritis: A Review of Literature
Pyelonephritis needs to be diagnosed early so proper treatment can be instituted to prevent further complications. If urinary tract infection is left untreated, it can spread to the blood stream.
Read More →
So ARE Nurses the "Nurse Police" When it Comes to Inpatient Hospital Stays?
This essay explains my experience with working with patients who face new dietary changes, in the form of heart-healthy diets, specifically. I explore my experience with acting in a sense, as a monitor of what my patient eats while hospitalized, monitoring food brought in by family and/or friends at the time of their visit, and how nurses should seek out teaching moments for imminent dietary changes their patients will face upon discharge home.
Read More →
Using Emotional Intelligence to Combat Nurse Bullying
Nurse bullying and incivility is an epidemic happening in all settings, including among nursing leaders. Many nurses admitted to being bullied in the workplace. The American Nurses Association defines nurse bullying as "repeated, unwanted harmful actions intended to humiliate, offend and cause distress in the recipient," calling it "a very serious issue that threatens patient safety, RN safety, and the nursing profession as a whole." Bullying and incivility contribute to decreased employee and patient satisfaction scores, increased nurse turnover rates, psychological and physical distress, and a lack of motivation and engagement. Bullying can be overt, such as verbal criticism, name-calling, and insults. Indirect bullying can be rumors, gossip, and sabotage.
Read More →
Enuresis
This article review covers enuresis and the behavioral factors that predict the severity of the disease as well as treatment responses. Medical and behavioral interventions, as well as limitations of the study, are discussed.
Read More →
Value of a Bachelor's Educated Nurse
Whether one is a recent graduate of an associate degree in nursing program or an experienced nurse who wishes to explore other opportunities in nursing. It is a good time to consider enrolling in a RN to BSN program and complete the BSN degree in nursing. In many cases, a BSN will open the door to opportunities in management, quality improvement, or be the first step in obtaining a Master of Science degree in nursing. In addition, some medical centers that hold Magnet recognition from the American Nurses' Credentialing Center (ANCC) require nurses to either have a BSN or begin school to obtain a BSN.
Read More →
Promoting Respect and an Environment of Civility in the Classroom
Educators today can attest to the lack of student respect shown in their classes. A lack of respect is a form of incivility. Since returning to in-person learning, respect has taken a nosedive. In fact, most of us have witnessed an increase of incivility in all walks of life. The question is, what to do about it? At a community college in upstate NY, the School of Nursing, Health & Wellness also noted a lack of respect displayed among students. The lack of respect was an issue the school felt strongly needed to be addressed. This prompted the creation of a Respect Committee with representatives from the Nursing Program, the Occupational Therapy Assistant Program and the Exercise and Human Performance Program to address the issue of student disrespect. To address the issue, the committee sent out a brief confidential survey to faculty and staff to investigate the prevalence of student disrespect, the facultys’ comfort with addressing student disrespect and established strategies for faculty to help guide them to promote a respectful environment for both teaching and learning.
Read More →
Enhancing Nursing Assistant Curriculum: Incorporating Strategies to Speak Up for Safety
Nursing Assistants are non-licensed clinical staff who, despite being directly involved in patient care, may be reluctant to call out safety concerns because of their position within the clinical hierarchal structure. The current nursing assistant training curriculum provides basic instruction on communication and teamwork skills, however, does little to reinforce the importance of the nursing assistant’s role, or empower these staff to bring safety concerns forward. This reluctance to speak up may result in unaddressed safety issues and patient harm.
Read More →
The Subtle Art of Connecting with Patients: Lessons Learned from a Seasoned Diabetes Nurse
The thing about patients is that they are humans filled with feelings. Even the ones who appear tough and stoic on the exterior; sometimes they're the hardest. Every patient is a person, a person who has decades of life experience. Just because we are trained in Nursing, doesn't automatically give us license to be authorities. You have to earn it. You have to earn that trust. You have to listen, really hear, and pay very close attention. There is a distinct art to inviting people to relate to you, and to enable them to trust you with their healthcare, their vitality, their life. It's a gift when you can connect with a patient. It is an honour. At the end of the shift after truly helping a person, a Nurse can hold their head high and know that they've made a difference. That's the sweet spot, that's the altruism of making a difference.
Read More →
What's the Deal With Being Unprepared? Patient's Should Know...
My husband has had 2 chest pain events within a week. As a nurse working primarily in cardiac nursing most of my career, I knew that any family member entering the arena of chest pain treatment would bear the wrath of my watchful eye. This has been An eye-opening, untoward (in my opinion), experience and an experience that can become a learning moment for many, as my skilled eye in emergency room settings can cause “jading” of an experience, but the perception should carry forward.
Read More →
Let's Look Back, at TEAM Nursing!
Team nursing while working as a new nurse meant 3 sets of eyes on our patient load. The RN was required to start I.V.’s, take off doctors’ orders and administer I.V. push medication, but the RN was ENGAGED directly in patient care under this style of nursing! The nursing assistant and the RN worked side-by-side to provide outstanding care to the patient without the RN (myself, in this example), feeling chained to the medication cart and having the feeling that taking time out for patient care would make me late for a medication pass. Perhaps other nurses in my era didn’t appreciate this style of nursing care, but in more recent days, primary nursing is the paradigm.
Read More →
Promoting the Nursing Profession Through Shared Governance
This article takes a historical look at the image of nursing from the days of Nightingale. The nursing profession is strained and incivility is on the rise. Now is the time to go back to the basics and look through the lens of shared governance to promote the profession and preserve its numbers.
Read More →
Weighing In On a Decade-old Subject
This writing addresses a subject of great interest to me. I unearthed an article written in 2011, by Ms. Tamekia L. Thomas, MSN, RN, PCCN, as per the time of a publication article dated Spring 2011: “Who’s Watching the Cardiac Monitor? Does it Matter?” (Nursing: Spring 2011- Volume 41) A quick background in my interest, is that I have recently retired after graduating as a registered nurse in 1988. One of the greatest joys of my nursing work, aside from the obvious patient contact and, hoping to make a difference to my patients’ experience, was working in telemetry. In several job locations, I worked telemetry intermittently, when assigned, though other duties notwithstanding.
Read More →
Addressing Health Disparities Among the Transgender and Non-binary Population Through the EHR: A literature review
Individuals who identify as LGBTQ face discrimination on multiple levels. One of those levels is in the health care industry. Nurses and providers are not aware of the importance of using proper terminology when addressing these patients. Using the pronouns chosen by the patient is one simple gesture that can make a difference. With the technology of EMR's chosen pronouns can be identified and utilized easily.
Read More →

Applying Current Standards of Wound Care Practice: Improve Patient Outcomes and Save Precious Time
By applying the principles of Moist Wound Healing we can provide patients with excellent wound care while saving precious nursing time and resources.
Read More →
So... How Can We Better Learn CPR?
An essay on how I think teaching CPR for the benefit of the science of CPR is more valuable than having nurses learn CPR online followed by manikin practice thereafter.
Read More →
Incorporating End-of-Life Content Early in BSN Programs
The purpose of this article is to address the need for nursing students to have more and earlier exposure to death, dying and end-of-life care in their BSN programs. Beginner nursing students often have their first client interactions in long-term care facilities, and it is where they are most often exposed to death. This usually happens before they have given death and end-of-life care much thought, let alone learned about it formally in the classroom. This article will highlight ideas for incorporating content into the classroom as well as give a greater understanding of the need for students to be exposed to all aspects of end-of-life care early and throughout the BSN program.
Read More →
The Art of Human Caring: My Lived Experience
I have spent nearly four decades in healthcare and have learned that if you want to be the best healthcare professional possible, finding balance is critical. Here I share my personal journey into nursing and leadership and the valuable lessons learned along the way. The truth is, they are just as valuable today as they were back then.
Read More →
A common link in the modifiable risk factors for severe COVID-19
Certain comorbidities, such as hypertension and diabetes, are often diagnosed once a patient has been hospitalized with COVID. Current thought suggests that these people had the medical condition, but it was not diagnosed until they were hospitalized. In this article I offer a reason as to why that may be. Based on this perspective, I further stress the importance of health maintenance in disease prevention.
Read More →
A Reflection on Authentic Leadership
Leadership reputations are made or lost during times of crisis (Chhaya, 2020). The Covid crisis has been one of the most difficult times for healthcare professionals. Leading during a tumultuous time can reveal character and strength but can also uncover leadership opportunities. In the following, we will review insights from this course, leadership purpose, and strategies to become an authentic healthcare leader.
Read More →
Maladaptive Strategies and Self-Harming
Information technology has become an ocean of opportunity for people of all ages to engage and influence how others feel about themselves and what they are doing. Not understanding appropriate boundaries and how to set them along with unhealthy coping mechanisms have left many people incapable of adequately dealing with a tsunami of criticisms. Unhealthy coping strategies increase the risks for self-harming behaviors.
Read More →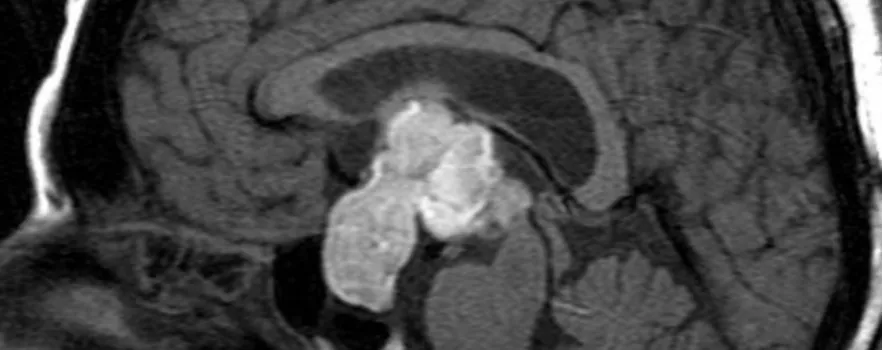
Sheehan Syndrome: What every woman should know
Sheehan Syndrome (SS) is associated with postpartum decreased functioning of the pituitary. Severe postpartum hemorrhage results in decreased blood supply to the pituitary leading to necrosis. The process leads to hypopituitarism, and subsequent decreased pituitary hormones. Deficiency of pituitary hormones manifest in a host of disorders which can cause high morbidity in women or even death.
Read More →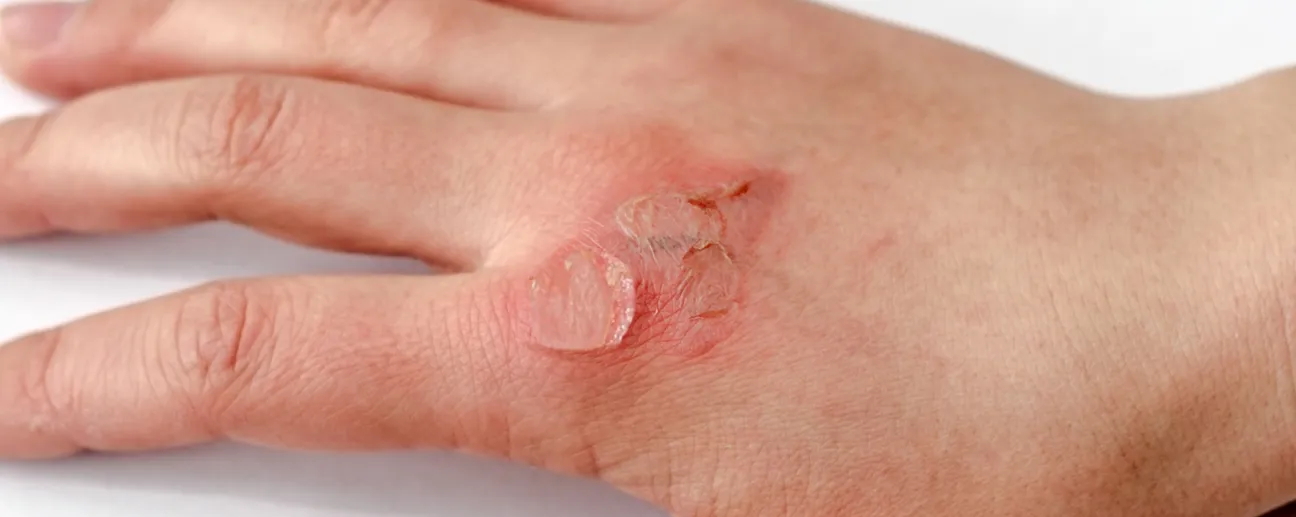
Why Skin Tears Are a Big Deal
Skin tears are the most common skin injury in the older population, but can occur in patients of all ages. It's important that clinicians are skilled at identifying individualized risk factors, interventions for prevention and the application of the most appropriate topical treatment.
Read More →
Exposed
Letter regarding a shooting at a medical clinic and the various exposures healthcare workers experience.
Read More →
How to Ace Online Classes for Nurses
An online class could be exasperating, especially when there are other distractions such as work, family, and life. DO NOT PANIC! Follow these simple rules to succeed in any online course.
Read More →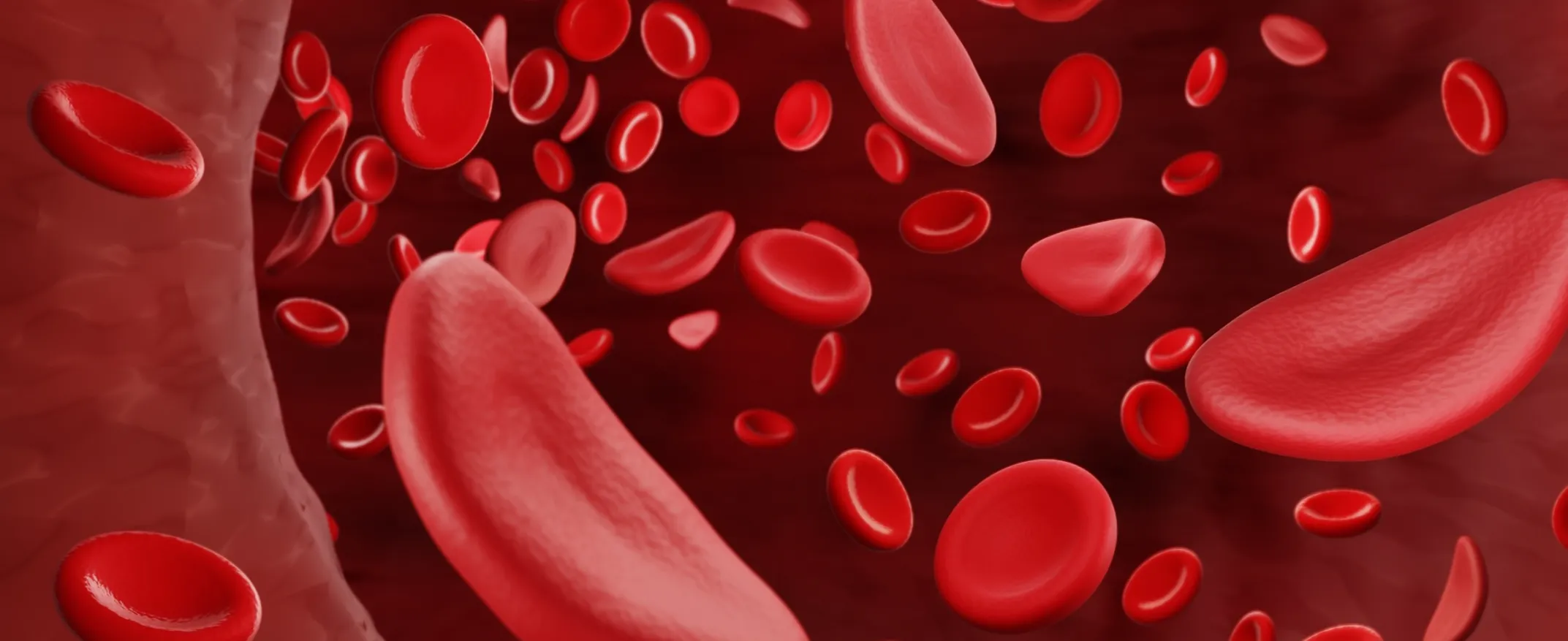
Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease is a debilitating condition secondary to the severe pain patients with this condition suffer especially when they are in crisis. This article includes the management and treatment of sickle cell disease and the diagnosis.
Read More →
Fostering Sound Relationships in Nursing Education Through Faculty and Student Mentoring
This article will provide a brief review of the literature on the benefits of effective mentoring such as improvement in the confidence level of novice nursing faculty members that leads to success as a teacher. This article will also provide an overview of some types of mentoring programs currently available. Further, this article will examine the importance of mentoring as it relates to enhancing the student-faculty relationship. Lastly, this article will examine ethical standards and the faculty member's role in promoting a just culture between the student, their peers, and the faculty member in the learning environment.
Read More →
Ethical considerations for the mentally unwell in a global pandemic
A case review on a mentally Ill patient during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Read More →
Evidenced Based Guidelines: Ischemic Heart Disease
Evidenced based guidelines to provide primary prevention and improve correct diagnosis and treatment.
Read More →
Case Study: A Systematic Approach to Early Recognition and Treatment of Sepsis
The term sepsis is often misunderstood. The public and often healthcare workers are unaware of the severity and high mortality rates this infection process has upon the world. Sepsis has vague symptoms that make diagnosis difficult. Often, sepsis is diagnosed in the later stages, when more obvious yet severe symptoms occur. This case study discusses a female who presents to the emergency department with sepsis secondary to pneumonia. Over the course of three days, the patient’s health quickly deteriorates, demonstrating the rapid progression of sepsis. Clinical findings, such as vitals signs, lab abnormalities, and symptoms of sepsis are discussed. The term bundle of care is presented to educate the reader on the golden standard of care for treatment of sepsis. This case study intends to increase community awareness and education to health care providers as well as providing an evidenced-based treatment guideline. More education and raised awareness will help prevent a deadly yet treatable infectious process.
Read More →
The Effect of Increased Nurse-to-Patient Ratios in Hospitals and Skilled Nursing Facilities Related to Patient Falls and Pressure Injuries
There has long been a debate between healthcare administration, politicians, payers and nurses on the issue of safe staffing and the effect of nurse-to-patient ratios in hospitals and Skilled Nursing Facilities (SNF). The purpose of this paper is to review research articles related to the effect of nurse-to-patient ratios at hospitals and SNFs on the fall rate and pressure injury rate of patients. It is the hypothesis of this paper that there will be a positive effect for patients related to the improved nursing ratios. Upon reviewing five solid research articles, as listed in the later part of this paper, the hypothesis is supported by solid evidence that both pressure injuries and fall rates of patients in the hospitals and SNF settings are directly improved by increased nurse staffing. The recommendation made from this review is that states improve regulations for hospitals and SNFs to increase and maintain adequate nurse staffing as it has a direct positive effect on patient outcomes.
Read More →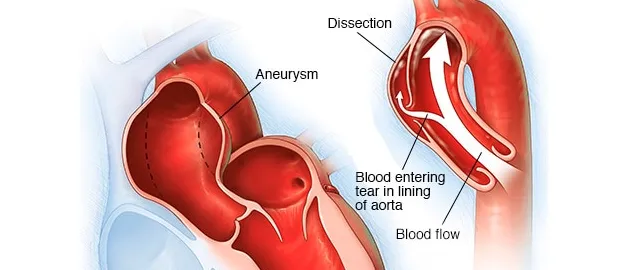
Immediate recognition of a dissecting Aorta
A summary of an encounter with a patient experiencing acute aortic dissection and recognizing an emergency.
Read More →
A Deadly Virus Provides Lessons to Learn
Like most of us, the COVID-19 virus has forever changed our lives. The virus is a wakeup call to reexamine life as we knew it; it is a chance for each of us to ask important questions such as, what makes us truly happy, what brings joy and peace in our lives and how can we make a positive difference in the lives of others.
Read More →
What Can We Do to Promote Professional Socialization in Nursing?
Transitioning to a new work setting is challenging for many nurses regardless of the time spent in practice. Promoting professional socialization, through mentoring and precepting, helps to facilitate a smooth transition. Effective mentoring, using role play, reflective exercises, and debriefing, provides the transitioning nurse the opportunity to self-actualize his or her potential in the new work environment. The use of Benner’s Novice to Expert Theory and Duchscher's Stages of Transition Theory as a basis for mentorship enhances safety and quality in the provision of care.
Read More →
Legislature Ought to Increase Rewards up to 10 Million Dollars to Whistleblowers who Combat Medicare Fraud and Abuse
The legislature ought to enact this proposed rule to increase rewards to combat Medicare fraud and abuse, in an attempt to increase more whistleblowers to come forward. Empirical research shows that this proposed rule has had the following good effects to increase rewards up to 10 million dollars to whistleblowers for reporting Medicare fraud and abuse and should therefore be seriously enhanced by legislature. The role of legislature in combating Medicare fraud and abuse to increase the amount of the rewards paid to whistleblowers whose tips about suspected fraud and abuse lead to the successful recovery of funds up to 10 million dollars. The intent of this proposed rule is to provide reward to whistleblowers in case of actual fraud or reckless disregard in the submission of claims.
Read More →
Wrongful Work Termination Because of Age and Sex Discrimination
Wrongful work termination based on age and sex should be prohibited in workplaces. Workplace discrimination occurs when an employer makes a job related decision to terminate employment based on characteristics such as sex and age, which makes it illegal. As a matter of fact, employment termination because of age and sex is prohibited by Congress, state, and local legislature. Federal and state labor laws exist to protect employees from workplace discrimination. Nowadays age and sex should not be a factor in termination of employment otherwise an employer will be liable for his/her actions. No worker, except certain executives, can be forced into involuntary retirement at a certain age, as people are fully protected by the law.
Read More →
Who Will Be Left to Care for You?
It is sadly too late to help many our front line healthcare workers who have contracted the deadly COVID-19 virus. We need to find a way to help the rest NOW in order to save their lives and in turn they can save your life.
Read More →
Strategies for Recruiting PhD in Nursing Students: Perspectives from a PhD in Nursing Graduate
Discussion relating to recruiting RNs into advanced education and particularly PhD programs.
Read More →
Crisis Management: Utilization of New Registered Nurses to Meet Healthcare Demands During COVID-19 Outbreak
During the COVID-19 outbreak, healthcare institutions are forced to enter into crisis management mode as demands on our healthcare system increase. While there are many nurses and healthcare professionals on the frontlines of this pandemic, the growing needs of the public may soon overwhelm our healthcare system. Could the best way to ease the current burden be new graduate registered nurses?
Read More →
Diabetes revisited: A review of the history, the current state of medical management and what the future may hold
This article reviews the history of Diabetes, the present day medical management, and research designed to control Type I Diabetes.
Read More →
Knowing Sepsis
Sepsis is a major challenge in the hospitals, one of the leading causes of death, It must be diagnosed early so immediate treatment can be instituted.
Read More →
Ethical Issues Raised When Parents Refuse Medical Treatment For their Ill Children
Working as a nurse, I am seeing ethical issues raises when parents refuse medical treatment for their ill children. Health care providers need rapid access to legal remedies in order to help children whose parents neglect medical treatment for their young because of their religious beliefs and hopes that a miracle might heal the kids. Despite those parents, who strongly stand by their point of view about spiritual treatment, doctors and state continue considering such point of view as futile, neglect, and abuse of the children. According to the doctors and courts, the medical treatment in ill children is more effective to cure disease in comparison to the spiritual means. As a society, we should make it a priority to protect children from parental neglect and abuse in case of withholding medical treatment, which in many cases leads to death.
Read More →
Mystery Diagnosis: Recognizing Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome (SS) is a rare condition that is believed to be induced by ingestion of serotonergic medications, leading to an increased serotonin level. Although many medications are thought to be responsible, some of the more common are antidepressants and opioids. There are no definitive tests to confirm SS, therefore diagnosis is based on clinical findings and can be somewhat difficult. A triad of symptoms, neuromuscular hyperactivity, altered mental status, and autonomic hyperactivity, are considered the hallmark signs, but are not present in all cases. Symptoms can vary from mild and almost undetectable to severe and life threatening. Three diagnostic systems are currently utilized to assist with diagnosis if SS is suspected: the Hunter, Sternbach, and Radomski criteria. A diagnosis of SS should prompt discontinuation of the suspected offending agent. Increased awareness of this issue is needed, including symptoms and risk factors, so that the advanced practice registered nurse (APRN) may promptly recognize and diagnosis this condition to avoid further complications. Completing a thorough history and physical, along with accurate medication reconciliation can assist the APRN in identifying high risk patients. While there is still so much about SS that remains unknown, current information and education on this issue will ensure the APRN is providing safe and high-quality care. Databases utilized were CINAHL, PubMed, and ScienceDirect. These databases provide access to numerous nursing, biomedical, and scientific journals and were useful in locating up-to-date, peer reviewed research on this subject.
Read More →
A Nursing Intervention to Enhance Wellness and Patient Adherence to Therapy for Headache - NEWPATH Study
The objective of the study is to ascertain whether the implementation of a nurse-initiated phone call between initial and follow up Headache appointments has the potential to enhance wellness and treatment plan adherence by reducing common barriers experienced by patients with Headache.
Read More →
Importance of Interprofessional Collaboration, Communication and Teambuilding
Collaboration is especially significant in the healthcare environment to meet the increasingly complex demands of patients with multiple co-morbidities. This article discusses the importance of interprofessional collaboration, communication, and team building.
Read More →
Quality Improvement in Pain Management
Discusses quality improvement approaches in pain management in the midst of the national opioid epidemic.
Read More →

Magnet Recognition: Is the Designation worth the Journey?
Currently, only eight percent of hospitals nationwide hold the title of Magnet Recognition (AHA, Fast Facts on US Hospitals, 2019) and even less receive consecutive designations. Eight percent is a marginally small number, especially when it comes to credentialing hospitals as havens for quality patient outcomes and centers of nursing excellence. The process of becoming a Magnet designated hospital is complex and grueling; requiring submissions of data, site visits, and taxes hospital resources in doing so. What then is this rare designation, and how does it improve both patient outcomes and nursing quality? Ultimately, does the designation provide benefit to those who obtain it?
Read More →
Cardiomyopathy: A Closer Look at the Disease
Heart disease is a wide term used for a variety of diseases that affect the heart. Heart disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Cardiomyopathy is one of the types of heart disease that affects about 50,000 Americans annually. There are four types of cardiomyopathy: dilated, hypertrophic, restrictive, and arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia (National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, 2007). This article will detail the different types of cardiomyopathy as well as the causes, treatment, sign and symptoms, diagnostic procedures and prevention. It will also cover ways to live with cardiomyopathy and end of life care.
Read More →
Love hate relationship in nursing
My experience from a person who hated nursing to emerging as a qualified nurse.
Read More →
Rapid Response Team to the Rescue
Rapid response team (RRT) purpose is to initiate immediate measures before patient deteriorates further and to educate the staff on activating the staff the Rapid response team.
Read More →
Impact of Language Barriers on Patient Safety
This paper discusses how linguistic differences can contribute to patient adverse outcomes and the role of health care providers in mitigating the impact.
Read More →
Clinical Algorithms and Leadership
Clinical algorithms can support the clinical practice of nursing staff. Nurses in acute care are expected to manage care for the acutely ill. The use of clinical algorithms can guide both new and experienced nurses with critical thinking and decision-making. The algorithms should be well organized and visually appealing. An algorithm should be re-evaluated after introduction into clinical practice, and further development should focus on its efficacy in producing a clinical outcome as well as by testing it in clinical education.
Read More →
Nurses Eat Their Young; An Insight Into Systematic Hazing and its Implications on Patient Care
I am a nursing student that worked as a CNA for six years. I was inspired to write this from my own experiences that I have encountered while working in the field of nursing.
Read More →
Perioperative Fasting Guidelines as it relates to ERAS Protocol: Exploring Existing Modalities
For the longest time, any procedure requiring anesthesia was accompanied with perioperative instructions mandating a fast from midnight until the surgery. However, anyone that’s lived long enough has learned to understand that just because something has been done for a long time, it doesn’t mean it should be done for the rest of time. With technological advances and improvements in research, medical practices and patient instructions should evolve. Here, we’ll explore the rationale behind the old modality as it pertains to preoperative care and instructions, what’s changed in research and technology, and finally, what new modalities should be learned, taught, and implemented.
Read More →
Retro-Clival Hematoma In The Pediatric Emergency Department
An unusual presentation of Retro-clival hematoma in the pediatric population
Read More →
Electroconvulsive Therapy in Pediatrics
The use of ECT for the pediatric population requires significant application of professional ethics in order for the process to be smooth and successful. Experts who administer ECT on psychiatric patients ought to consider the right of the patient to choose the type of treatment they want after being equipped with all the pros and cons related to the process.
Read More →
Health Care Leadership
An active leader can create an environment that fosters members of the group to develop their skills and imagination, so that they can succeed at the tasks and vision for the organization.
Read More →
Knowing Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury
Transfusion-related acute lung injury occurs within 6 hours post transfusion where patient develops shortness of breath without signs of pulmonary overload in chest xray. With evidence of hypoxemia / low oxygen saturation.
Read More →
A Husband's Difficult Decision
A husband's difficult decision regarding his critically ill wife and DNR status
Read More →
Preventative Community Health Improvement plan
Preventative community health improvement plan to reduce the number of cases of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs).
Read More →
What Are The Effects Of Floating to Nurses And Patient Care
This article will explore how floating affects nurses and what management can do to help nurses relieve the stress, anxiety, and dissatisfaction of the nurses with the health care system.
Read More →
From Registered Nurse to Field Reimbursement - A Surprising Path to Patient Advocacy
When I took the oath of a nurse, I promised to be an advocate for patients. I never imagined that keeping this oath would lead me out of my bedside scrubs and into a suit as an FRM.
Read More →
Managing the Inevitability of Change
Change is inevitable. Whether we are changing our minds, our clothes, or a channel on television, we know change happens… and we are fine with it, when we are the ones enacting it. However, what about when change happens to us? This article explores the effects of a hospital’s unit closing on staff – the good, the bad, and the ugly – and seeks to identify ways to mitigate the bad and ugly emotional responses, and hopefully explore means of increasing the good (by both hospital management practice, and individual mindset). A unit in one of south Florida leading hospital serves as a case study as we delve into this topic.
Read More →
Everything you need to know about Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
This article is about everything you need to know about Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. What is CFS, what are its causes, the symptoms and the remedies?
Read More →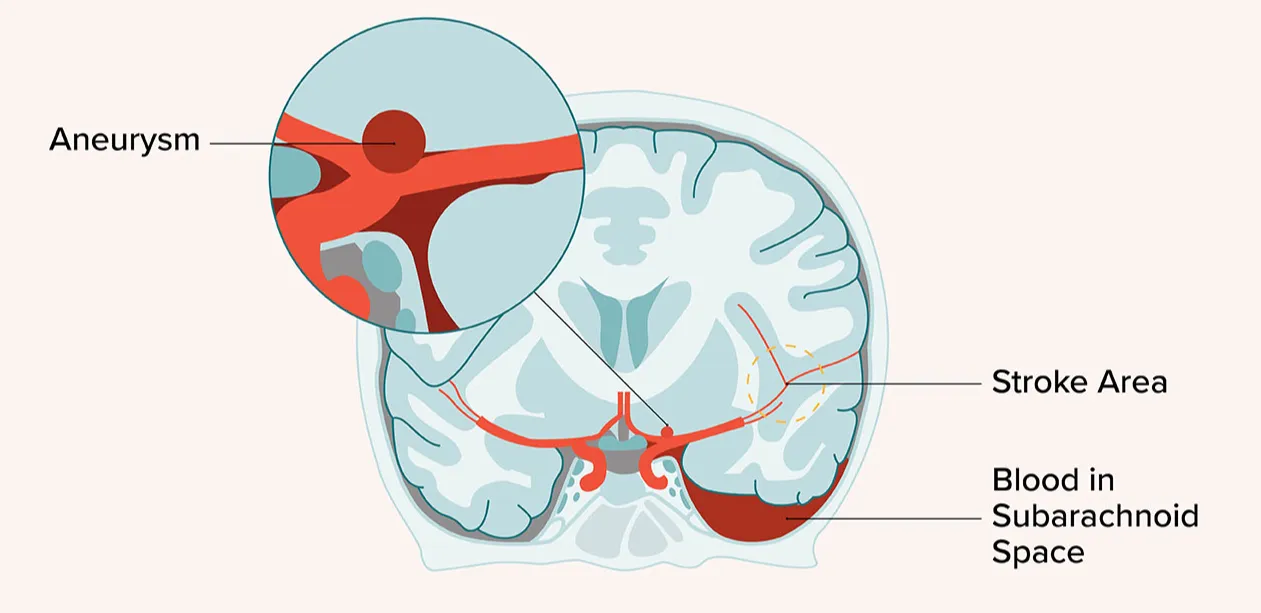

Disease Preveniton and Health Promotion Screening: Breast Cancer
Current risk factors for breast cancer, screening recommendations, and latest diagnostic assessments.
Read More →
A Review of the Treatment for Postoperative Nausea and Vomiting
Common treatments reviewed for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting, mostly in the PACU phase of care.
Read More →


Patient's Wishes and Dying with Dignity
After the palliative care made rounds on the afternoon shift, they were able to get a hold of Mr. D’s only relative: a niece who was not close with him but apparently had called the ambulance for him to come to the hospital.
Read More →
RN's informed about skills of Occupational Therapist & Physical Therapists
Registered Nurses do not differentiate between the applied skills of the Occupational Therapist and Physical Therapist, nor do Registered Nurses realize it is the Occupational Therapist who is responsible for prescribing patients with developmental disabilities the type and configuration of an appropriate wheelchair.
Read More →
New Innovation for Chronic Kidney Disease
This body of work looks at new and innovative treatments that are being researched and developed for the treatment of chronic kidney disease.
Read More →
The Virtual Professor
Today many colleges are increasingly using online approach to provide effective and easily accessible education to attract students from wide geographic areas and increase enrollment. The virtual professor is constantly required to monitor and supervise students who are not visible in a virtual learning community.
Read More →
Regional anesthesia; A quick introduction
This article offers a small introduction and overview regarding regional anesthesia. You have nerves that run all through your body. Nerves provide a pathway for impulses to communicate between the brain and other parts of your body. Not only do your nerves tell your muscles to move, they tell your brain when something is painful.
Read More →
Skin - A Poem
This poem is about my emotional reaction to a dermatological visit with my FNP, DCNP.
Read More →
Post-Fall Care Nursing Algorithm
Post-Fall care practices are an integral aspect to patient care. As we care for older adults it is important to consider post-fall care practices.
Read More →
Factors Influencing Nurse Medication Errors
This article explores the medication errors and the phenomena of nurse distractions. Nurses are intimately involved in the medication administration process. Even though the parameters of selection, dosing, compounding, and dispensing medication remain under the purview of other allied health professionals, the nurse represents the last safety checkpoint between the medication and the patient and efforts should be directed toward removing obstacles which are negatively impacting this process. It has long been suspected that nursing distractions whether by patient, family, coworkers or others, are facilitating the occurrence of errors in the hospital setting. There are practices which are discussed which may ameliorate this threat to some extent if employed consistently and judiciously.
Read More →
Improving the Clinical Experience of Working with Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Team Approach
This article emphasizes the value of working together in training the future nurses, and suggests strategies and tools to assist in the process. Bringing quality and safety to nursing education in the classroom and clinical is of high importance. Staff nurses play a key role in the clinical preparation and success of the student nurse. Faculty, preceptors, students and the system at large can be more successful if working together to reach the learning objectives and goals. Designated educational units (DEU) are an example of improved clinical teaching/learning environments, but every clinical unit can participate and practice quality regardless to the formal structure and protocal of an established DEU. Understanding that the staff nurse plays a significant role in mentoring the future nurse generation is a reason enough to see working with students is a necessity rather than a burden.
Read More →
Use of Digital Technology for Heart Failure Patients
The benefits of technology assisting the heart failure patient.
Read More →
Nursing Speciality Certification
The benefits of nurse certifications for the nurse, hospital and patient.
Read More →
Why is Psychiatry so Taboo?
In almost every society, psychiatry has an adverse stigma attached to it. Any form of mental illness is perceived as a sign of weakness. In some cultures, psychiatry is not considered an important or prestigious form of medicine. To acknowledge the importance of psychotherapy is to recognize that the members of the society may have some mental abnormality. There is a thin line between sanity and insanity. So to concede that something is wrong with one' relatives is the admittance that one may be inflicted with the same disorder.
Read More →
Recovering from Tragedy and Surgery
A story of a patient recovering from surgery and a tragic event.
Read More →

Medical Equipment
This article is about receiving a patient postop who required oxygen. The respiratory therapist had disconnected the oxygen and placed onto the beside portable O2 tank to administer a nebulizer treatment. After nebulizer treatment was completed the oxygen was not moved back to the wall and tank went empty. The patients oxygen dropped.
Read More →
Multimodal Analgesia: Ways to Take Away the Pain
This article addresses ways to use multimodal analgesia such as opioids, anti-inflammatories, regional anesthesia, etc to achieve greater pain control in patients.
Read More →
Current and Future Educational Challenges for the Nurse Educator
This article explores current trends in nursing education.
Read More →
Characteristics of various Nursing Paradigms and nursing theories within the Totality and Simultaneity Paradigms
This paper is an attempt to explore the conceptual basis and characteristics of various paradigms in nursing. It will exemplify how nursing theories and models fit within a certain nursing paradigmatic classification. Therefore, this paper will also present an example of how various nursing theories fit within the totality and simultaneity paradigms.
Read More →
Is Reform Needed in License Disciplinary Procedure?
Discussion of disciplinary proceedings in California and the need for changing harsh disciplinary standards.
Read More →
Factors Influencing Job Satisfaction in a Population of Critical Care and Emergency Nurses
An exploratory study examining the contributing factors to nurse job satisfaction.
Read More →
The Importance of Educating in Real-Time
Working in the acute care hospital, provides many opportunities to learn. As healthcare workers, we must recognize and act quickly on any situation that puts a patient at risk. A recent situation occurred in the hospital that required both the need to act and to provide education in real-time.
Read More →
Polypharmacy Mitigation: A Lifetime of Education
An informational article on the issue of paolypharmacy and medication redundancy in todays healthcare and the use of education over the lifespan as a corrective measure.
Read More →
Building Trusting Work Relationships in Healthcare and Beyond
In an effort to help leaders in various types of healthcare organizations learn how to build trust and strong work relationships within their organizations, eight chief nursing officers (CNOs) from healthcare organizations throughout California were interviewed. All the CNOs were asked the same structured questions. A review and analysis of those interviews revealed the following five dimensions as key ingredients: authenticity, work ethics, communicating and sharing news, history and reputation, and creating a supportive and empowering environment. Our results include the definitions of trust by the eight CNOs, the Four R’s of building trustworthy relationships and an acronym of SHARE. We discuss what CNOs describe as “trust blockers,” actions a CNO can take that would break the employee’s trust. The results of this research can be used in a variety of ways including incorporating them into leadership development training aiming at strengthening their personal leadership styles and improving workplace environments by creating and role modeling a more open communication culture.
Read More →
Pregnancy in African Cultures
Pregnancy and birth are celebrated in every part of the world. In African cultures, because of many superstitious beliefs, many families will perform different rituals to safeguard the pregnancy. Pregnancy is acknowledged but not celebrated.
Read More →
Night Shift Nursing: A Policy Proposal
Night shift nurses face many obstacles in achieving adequate work-life balance. Additionally, there are ramifications for night shift nurses in that health problems may appear after extended time working the night shift. This research puts forth some possibilities for changing this culture and making nursing and nursing care safer for patients and caregivers.
Read More →
Scope of Advanced Practice for Nurses in the United Kingdom
A 3,500 word article which critically discusses advanced practice for nurses within the United Kingdom. This was originally written for an MSc in Advanced Practice.
Read More →
Health and Wellbeing: A Student Nurse's Perspective
This essay discusses health and well-being as multifaceted concepts and explores how my health and wellbeing has been affected since becoming a student nurse. This essay also discusses the importance of maintaining good health and wellbeing in relation to self-care and patient care.
Read More →
A Nurse Fighting Terror with Love
In Jerusalem area on January 17, 2015, Dafna Meir, of blessed memory, mother of 6, was a nurse who treated Jews and Arabs. Before she was murdered by a terrorist she composed this touching prayer.
Read More →
I Will Not Die But Live!
Since leaving nursing in 2008 I have wanted to write about my experiences as an emergency nurse and what happened to me as a whistleblower. This is my story.
Read More →
Amongst the Angels
Most women enter the hospital and leave with wonderful pictures and memories. Their infant bundled tightly in their arms and their vehicles await them to whisk them away to the sleepless nights as the parent of an infant which all too soon turn into the sleepless nights of the parent of a teenager. But there are those few mothers who are wheeled to their vehicles whose arms are empty and whose infant spirits reside in the arms of the angels and whose bodies rest in Pathology awaiting their final destination. It is my job to receive these infants and let them rest until they are transported. I work amongst the angels.
Read More →
Inspiring Leaders
Characteristics of a successful nursing leader include adaptability, authenticity, and supportiveness. Leaders inspire employees with a vision, while managers provide direction to employees.
Read More →
Young and Healthy in the PACU
Some patients in the post anesthesia care unit (PACU) are young and or very healthy. These qualities sometimes give the impression that there will not be complications from surgery or anesthesia. This is not always the case. These patients may be overlooked for experiencing complications because they are healthy. I have seen a number of patients who have no health problems experience side effects from anesthesia and surgery.
Read More →
Story of Sarah
Story of a senior nursing student caring for a client dying and her emotional struggles.
Read More →
Attitude Matters: Attitudes and Values in Nursing
Even with a shared set of values and behaviors, we cannot underestimate the nurse’s attitude towards: others, their patients, their co-workers, and the organization they work for and towards the profession of nursing.
Read More →
Use Critical Thinking: It takes Only a Second for an Error to Occur
Working in an acute care hospital, provides many opportunities for learning. As healthcare workers, we must recognize and confront situations that put our patients at risk for harm. A recent situation occurred in the hospital that did provide an opportunity for learning and the need for an action plan.
Read More →
Caring Behavior of Nurses in Orthopedic Wards of Selected Health Institutions As Perceived by Patients
To identify Nurses perceived behavior as caring by patients during Hospitalization.
Read More →
Missionary nurse in the jungles of Honduras
With our imminent move to an entire other continent, and with new ministries to start, and new “adventures” to seek, I find myself contemplating my time in God’s service over the last 15+ years... and I was reminded of this story...
Read More →
Increasing demands on nurses and the role of the nurse educator: Developing nursing competencies
Increasing demands of todays healthcare environment poses many challenges for nurses providing care at the bedside. Nurse educators are in a position to develop nursing competencies that support nurses and assist them in the provision of safe, quality patient care.
Read More →
Respect: A Duty One to Another
In a time of nursing strikes, it is imperative that we respect each other as a profession. This articles explores the roles of staff and strike nurses.
Read More →
Preparation of Faculty in the Era of Educational Technology
While online nursing education programs are on the increase, faculty is constantly challenged to teach effectively in online environment. Preparation of nursing faculty in educational technology provides avenues for successful online teaching.
Read More →
Practicing Holistic Nursing as Intensive Case Management
Case study describing management of mentally ill client using holistic nursing methods.
Read More →
When "Old Dogs" go Back to School
I went back to college at the age of 62. Being an "old dog", I was not computer savvy, so taking classes mostly on-line was quite challenging. I believe that my trials and triumphs evidenced in this article, will encourage nurses, especially older nurses, to go back to school for their BSN.
Read More →
My Teaching Learning Philosophy
My philosophy of teaching learning revolves around the profound belief of Peter (1965). I strongly believe there are certain responsibilities of teachers to make teaching learning effective. First of all, educators must create a difference between education and teaching. Secondly, teaching learning process must be student centered. It must provide opportunity to students to learn according to their interest and needs. Further, students are also responsible for their own learning. Based on my teaching learning philosophy, I can recommend to bring immediate change in our teaching learning environment we need power and authority which now I can bring as a nurse educator.
Read More →
I Wonder If?
A vignette reflecting the effect of the registered nurses effect on a chemotherapy patient.
Read More →
Do Nurses Need Biology?
As Biology instructors for nursing students, it is an honour to contribute to laying down a foundation in Biology for future nurses. One common question that has emerged among nursing students is “Why do I need to know Biology if I’m going to become a nurse?” We have wrestled with this question for some time. How does one generate an appropriate response to this question? How does one instill within a student the passion for learning Biology? How can one emphasize how valuable understanding Biology will become in the workplace? We hope to raise some interesting discussion and awareness about a topic that we have spent countless hours deliberating amongst ourselves and our colleagues.
Read More →
Six Sigma and Healthcare Finances
This article is a brief primer on Six Sigma methodology and its impact on healthcare finance and nursing.
Read More →
Are Canadian Nurse Practitioners here to stay?
This paper outlines articles that take a closer look into the role of NPs in the Canadian health care system, and how their roles have evolved in response to an ever-changing health care environment.
Read More →
Interactive Technology is Shaping Patient Education and Experience
This article describes the Nurse Informatics participation in adopting technology in patient care and nursing workflow. Healthcare settings now integrate electronic medication prescribing, tele-health, online appointment scheduling and mobile laboratories where informatics nurses are essential in guaranteeing that the computerized solutions interface with each other. In order to accomplish information related activities, informatics nurses must synchronize and exchange significant clinical and technical information with the goal of supporting and coordinating safe, effective patient care and assuring an efficient workflow. A strong foundation for addressing the challenges of electronic documentation is the informatics nurses capability to understand and direct the balance of patient care with the technology systems and organizational structure that supports this balance. In order to guarantee a successful implementation of a computer system while managing patient care is to integrate nurses’ perceptions, beliefs, and knowledge in the use of new technology and how nurses implement this technology into their daily nursing practice.
Read More →
Bedside Reporting: Embracing the Need for Clinical Change
Communication is an integral part of nursing care. The implementation of bedside reporting practices provides an avenue for best practices and improved outcomes.
Read More →
9 Steps to an Exceptionally Happy Day at Work
Nurses are practical and purposeful. When your job is managing the well-being of other people it can be tough to put yourself in the schedule. Most nurses I know find caring for everyone else easy and the very thought of taking care of themselves may seem selfish. Yet, to achieve true balance one must learn to receive in the cycle of giving.
Read More →

Women and Homelessness
Women and homelessness is a great concern that affects the global policy and health determinants to improve health. This case study is a glimpse of the cultural class as it revolves around the lives of mostly White homeless mothers, attending to both everyday lives and cultural norms while exploring and interpreting their interdependencies.
Read More →
Beginnings of a Lifetime
Inspirational article about becoming a nurse and 38 years later.
Read More →
My Love Affair with Pain: A Lyric Essay
"My Love Affair with Pain" is a lyric essay that chronicles my relationship with chronic backpain. I wrote this as a creative writing essay, but after I read it at a seminar, several nurses approached me and asked if they could use my essay in their nursing classes to help nursing students understand the depth and breadth of pain.
Read More →
Yoga and the Benefits to Adults with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
A leading cause of decreased quality of life and debility due to diminished gas exchange, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) progresses slowly with no known cure. The overall effect on other systems and the emotional toll placed on these patients makes activities of daily living exceedingly impossible to manage. The purpose of this article is to conduct a review of the literature to determine the benefits derived from practicing yoga on one’s quality of life and pulmonary functions for those diagnosed with COPD with a special focus on the author’s current practice in home health. In addition The Yoga Sutra and Bhagavad Gita will be reviewed to offer a holistic approach to care.
Read More →
Dear Health Care Professional taking care of my mom with Alzheimer's disease
A manuscript geared to those caring for patients with Alzheimer's disease.
Read More →
The Role of Nurses in Home Health Care
The role of a Home health nurse is unique, exciting and sometimes very challenging. With the demand for a safe, cost-effective and quality health care by the consumers, the home health field is the future of health-care. Home health-care nurses make a significant impact and contribution to the health-care industry, the community, and to the lives of their patients and their families.
Read More →
Was "Winnie-the-Pooh" mentally ill? An Interesting Assignment to Learn about Mental Illness
When you assess and analyze some of our favorite childhood cartoon characters some of them display signs and symptoms of mental illness. This assignment engages students to learn about what defining characteristics to look for when assessing patients for mental disorders and just how subliminal messages especially those that are negative can be harmful to our well-being.
Read More →
When Doing The Right Thing Leads to the Wrong Results
Reprimanding nurses for medication errors contibutes to a culture of evasion and silence and does not address the reason behind the mistake.
Read More →
Provision of Effective Patient Education: A Learning Clinical Experience
Patient education is one of the fundamental aspects of holistic nursing care. It is the core responsibility of nurses to provide information to the patient and their families that is understandable and appropriate promoting awareness and optimal health. However, student nurses come across to various barriers in providing effective patient education, including decrease knowledge, lack of clear objectives and lack of clinical exposure. Similarly, I came across a similar situation in my community rotations in which I faced obstacles in educating the patient. There are several strategies that results in the provision of effective patient education, which includes, open communication style, written instructions, addressing barriers, formulating teaching plans, identifying learning styles and needs, and use of teaching aids. Therefore, through effective patient education nurses can increase the independence of client for self care in hospital as well as in community settings.
Read More →
Views of a New Graduate Nurse: The Value of Mentorship
A brief overview of one nurse's struggles as a new graduate nurse and the importance of improving the working environment for new nurse graduates.
Read More →
Anesthesia Awareness for Perioperative Nurses
Anesthesia awareness definition is an unexpected recall of events while under general anesthesia. The majority of the authors place the rate of anesthesia awareness to one patient out of every one thousand patients that experience some form of anesthesia awareness, however the exact mechanism of the pharmacological action of anesthetic is not clearly understood.
Read More →
Phlebotomy Basics For Nurses
The processes of phlebotomy are pivotal for patient care. Nurses may have to perform phlebotomy for their patient in various health care settings. Understanding the procedures, processes and reasons behind phlebotomy is the key to ensuring patient safety and positive patient outcomes.
Read More →
Grandma and What She Taught a Hospice Nurse
One of the most rewarding and difficult experiences of my hospice career was helping my grandma to pass peacefully.
Read More →
Insuring the Uninsured: Hispanic Communities
Despite the improved enrollment from 2014, there are still a percentage of the population that remain without insurance. The Hispanic population continues to be the largest population that have not enrolled and recent limited data indicates a variety of reasons. The biggest promoters of health care are the individuals that provide the service. In order to promote enrollment, we need to use health care providers and nurses to be a resource, the educators and the “sellers” of Affordable Health Care.
Read More →
Tourette's Syndrome: Implications for a Moving Disorder
This article highlights the subjective, objective and recommended nursing treatment for Tourette's syndrome.
Read More →
Nurses Don't Eat Their Young - Unless You Believe It
This article discusses that through early nurse conditioning, new nurses are set up to believe that experienced nurses “eat their young.” This conditioning perpetuates the stereotype and thus becomes part of the problem and culture. One new nurse’s journey to deny this teaching and be open to experienced nurses’ help and criticism may prove that an adjustment in perspective and how we begin to teach new nurses to relate to experienced nurses might help change this culture and the new nurse’s first year on the floor.
Read More →
Charles Bonnet Syndrome: What Nurses Need to Know
Charles Bonnet Syndrome is frequently the appearance of visual hallucinations in psychologically intact people. Studies estimate the prevalence of these hallucinations of at least 10% of the elderly with vision impaired by, for example, macular degeneration or glaucoma. The syndrome is frequently undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. This case study shows how a patient's symptoms were misinterpreted causing unnecessary stress to the family.
Read More →
The Future of Nursing Education: Heading for a Major Crisis
Nursing as a practice and profession has experienced significant changes over the years. For instance, in the 1800s nurses were expected to be subservient to doctors. Just hear what the doctor who gave Springfield Hospital’s first nursing graduation address: "Every nurse must remember that it is the attending physician's business to make a diagnosis of disease and hence that she should never hazard an opinion herself, under any circumstances." (Dr. Hooker, Springfield Hospital Annual Report, 1894). It would be interesting to know what the nursing faculty were thinking when they heard those words. Thankfully nurses during that era did not take the doctor’s advice and remained dedicated to advance and advocate for the profession of nursing. Around the same time that Springfield Hospital’s first nursing graduating class were listening to their graduation address, Florence Nightingale along with other nurse advocates, were making incredible strides to implement nursing education. After the Crimean War, Florence Nightingale recognized and introduced the need for formal nursing education but the education was limited to basic nursing knowledge and skills. As a result of the Women’s Rights Movement in the 1900s, the idea of nursing as a profession evolved into a reality. As society’s healthcare needs changed, nursing education had to change to meet those needs. There were however, challenges each century faced when trying to ensure nursing education met society’s needs and today, the challenges faced are heading right for a major crisis.
Read More →
A Competent Psychiatric Nurse: What role does empathy provide in competency?
The fundamental foundation in initiating competent skills as a psychiatric nurse is similar to any specialty in nursing. We must implement the necessary processes of providing the standard of care by using the method known as the nursing process. To successfully implement these steps it is necessary to seek understanding of the clients’ individuality which takes effort, establishment of rapport, and time. Empathy is an essential factor to obtain accurate data, individualize interventions, and best outcomes addressing the clients’ uniqueness. As a psychiatric nurse one noted that empathy plays a significant role in providing competent care and optimizing positive outcomes for my acute mentally ill clients.
Read More →
If You Work in a Hospital - A Poem
I have been retired almost 3 years. Since retiring, I have been writing poetry instead of clinical records, reports, and contract proposals. Some of my poetry is about work. This poem reflects my experience working with nurses and doctors. I appreciate that poetry is not something you usually publish, however, like a photo, a poem is sometimes worth a thousand words. I think this poem is particularly relevant to the nurses who read your magazine, it has to do with bad days at work, and high expectations regarding patient outcomes.
Read More →
Disparities in Healthcare: Night Shift Nurses
Night shift nurses have been shown more likely to developing health issues than their day shift counterparts. Research over the past twenty years has led to the increasing conclusion that working night shifts for as little as eight shifts a month is associated with an increased likelihood to develop metabolic syndrome, a four-fold increase in the incidence of vascular events, and an increased chance of developing certain cancers.
Read More →
Therapeutic Hypothermia Management
The leading cause of death in North America is heart disease, resulting in 611,105 deaths in the last year. Cardiac arrest accounts for more than 300,000 heart disease related deaths. Patients that receive early quality chest compressions and defibrillation present with increased survival rate, however, the degree of brain dysfunction varies. The advancement in cardiopulmonary resuscitation after cardiac arrest and the use of therapeutic hypothermia have minimized brain injury and improved neurologic outcome. In 2002, two studies demonstrated the use of therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest proving to lower mortality rate and have neuroprotective effect. This led the American Heart Association and the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation to recommend the implementation of therapeutic hypothermia after the return of spontaneous circulation post-cardiac arrest. Mild hypothermia is also utilized in traumatic brain injury to control cerebral edema and to decrease intracranial pressure (ICP), cerebral ischemia, and subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH). However, clinical effectiveness for subarachnoid hemorrhage is still questionable. This paper will focus on the recommendations for therapeutic hypothermia after cardiac arrest as well as a briefly discuss its use for clinical trials in traumatic brain injury, cerebral ischemia, and SAH.
Read More →
It is Time to Recruit More Men into the Profession of Nursing
It is a benefit to have men working in the profession of nursing. We need to recruit more men into our nursing schools and to work in our healthcare institutions. Both male and female nurses bring different perspectives and benefits to the profession of nursing and to the patient’s they care for. The ability of men to negotiate and obtain higher salaries and positions in both administration and nursing specialty areas may serve as the impetus to elevate the entire nursing profession.
Read More →
The Forgotten Arm of Care
This article addresses the need for building a healthy work environment amidst the great emphasis on staffing to enhance care .
Read More →
Recognizing Heart Disease As a Women's Disease
There are noted differences among heart disease signs between men and women. Coronary Heart Disease can go unnoticed in women until they actually suffer a heart attack (NIH). Thus it is essential women are aware of the signs and symptoms, risk factors and healthy life style choices to prevent the devastating effects of heart disease. .Seeking early treatment when symptoms present is vital in improving the outcome of heart disease. It is important to teach women how to incorporate prevention strategies such as: consuming a healthy diet, maintaining optimum weight, maintaining an active lifestyle, maintaining both normal blood sugar and blood pressure levels as well as avoiding risk factors such as smoking, drinking alcohol limit their stress and any unhealthy behaviors that can lead to heart disease. Advocating for women and promoting education regarding health issues affecting women needs to be a priority so heart disease in women can be prevented and effectively treated.
Read More →
DNP and the Transformational Leaders
Transitioning advanced nursing practice to the doctoral level represents the natural evolution of the nursing profession and the right moves to ensure that nurses are prepared for the highest level of practice. Many advocates within the health care community (local and national authorities) are calling and welcoming the DNP role. National and state agencies, as a leading advocate for advanced practice nursing, understands greatly the contributions APNs (advanced practice nurse) make in the health care system as cost-effective providers. In addition, APNs have identified the need for additional education in the areas of evidence-based practice, quality improvement, and systems management, among others (Kaplan & Brown, 2009). This transition in the education of advanced practice nurses (APNs) is targeted to meet the increasingly complex needs of patients, families, and communities in a rapidly changing health care environment. DNP education also has the potential to transform the nursing profession in a variety of ways. These include: • Creating and adopting new roles in nursing practice • Increasing the influence of APNs in health care and policy development • Promoting leadership by APNs in their workplace and health care organizations • Enhancing the self-concept of advanced practice nurses • Strengthening inter-professional relationships and collaborations. (Kaplan & Brown, 2009; Swider, Levin, Cowell, Breakwell, Holland, & Wallinder, 2009) The DNP stimulates the creation and adoption of new advanced practice role. As health care becomes more complex, it will take such strong leadership criteria for nurses in all fields to continue to improve their own standards and the qualifications of others in the field (Kaplan & Brown, 2009).
Read More →
When does treatment become a life sentence?
This is an article based on patient's autonomy and dignity and the treatment process for those that have terminal illness.
Read More →
The Other Side of Healing
A glance back at how I came to appreciate the special role a nurse plays in helping patients experience a peaceful death and assisting family members through the experience.
Read More →
Nursing School Angel
How a patient in nursing school taught me how to deal with life and death
Read More →
Improving Patient Care While Decreasing Costs: The Benefits, Barriers, and Student Perspectives on Nurse Residency Programs
Many professions have long since realized that a vast divide exists between the classroom and real-world practice and, thus, have mandated transitional programs. Nursing lacks such an intermediate step as part of its professional training although new nurses are pressured to provide both safe and competent care to increasingly complex patients without any transitional support. To fill this gap many institutions have begun to implement their own nurse-residency programs [NRPs]. However, since not all institutions have introduced such transition-into-practice programs barriers must exist. Nationwide, NRPs are shrouded in confusion, false perceptions, and concerns that hinder their implementation. This manuscript was compiled to help shed light onto the reasons for the lack of implementation and provides evidence of the importance and overall benefits for such programs. Personal perspectives are also provided from the authors in order to gain a nursing-student perspective about these transitional programs.
Read More →
Successful Aging For Canada's LGBT Older Adults
A research paper I wrote for my BSN degree regarding how health care services, particularly nursing can accommodate older adult members of the LGBT community and provide safe and best practice care.
Read More →
My Pet Rock and Other Fictions
Mother of son with severe disabilities explaining to her daughter why parents never divorced as they & the family experienced the tragedy of a brain damaged son.
Read More →
Haddon's Matrix and Falls Prevention
Haddon’s Matrix is an injury prevention tool that has been utilized for analyzing and preventing injuries related to auto accidents, snowboarding, and water safety, among others. A review of the literature revealed no use of Haddon’s matrix with regard to patient falls investigation or prevention. The purpose of this brief communication is to introduce the potential utility of the matrix for falls prevention and investigation.
Read More →

Family Presence during a Code Blue
I have been a nurse in the Cardiac Intensive Care Unit for over five years now, and have participated in many code blues. Some of these situations are appropriate for family to attend and some are not. Each situation is assessed individually to determine the appropriateness of family presence.
Read More →
Reflections of Nurse Educator
Teaching is an art. Some people are born teachers while others acquire the skill. To be a great teacher, one has to have a sense of humor and be very flexible. Teachers will never teach to gain monetary reward. However, they will teach to achieve the best reward - satisfaction that they have an impact on the education of the leaders of the world, the training of CEOs, and the success of new breed of professionals. Teaching is a noble profession.
Read More →
Prescriptive Authority for Nurse Practitioners
The physician shortage in primary care, plus the growth of nurse practitioners and increasing need for access to health care, creates a necessity for more autonomous nurse practitioners. However, current restrictions on nurse practitioners, particularly prescription regulations for controlled substances, limit what practitioners can do for patients. These restrictions also increase wait times for patients and have the potential to increase liability claims as physicians prescribe medications for patients they have not adequately evaluated. Nurse practitioners have proven to be a safe, quality, and cost saving approach to primary care. To meet the growing needs for patients, nurse practitioners must have the ability to prescribe controlled substances in all 50 states.
Read More →
Is Nursing a Profession?
Professions require that educational preparedness must be within institutions of higher learning. In order to be held out as a profession, an individual must be able to practice autonomously within their scope of practice. Nurses have an identified scope of practice mandated by a particular state board of nursing. A profession has a code of ethics which is recognized across numerous levels of practice within the profession. The culture and norms of a profession are easily recognized by the professionals who make-up the body.
Read More →
The Nursing Image: A Position Paper
The nursing image connotes a healing caregiver at a patient’s bedside. Nursing as a highly skilled and education profession remains incongruent with media and advertising portrayal of the nursing image, in contrast to published reports as the most trusted profession for the past decade. Current public perceptions of the nursing image are sharply contrasted to that of how nursing prefers to be viewed. This purpose of this work is to edify two contrasting positions of the ethical constructs of the nursing image as well as present posits of the author.
Read More →
Why Do Nurses Eat Their Young?
This article discusses issues related to new nurses regarding bullying and how the problem can be solved.
Read More →
Barriers to Patients Undergoing Methadone Maintenance Therapy
Methadone maintenance therapy is one method utilized to combat opioid addiction and is an effective treatment in the abstinence from opiates. The purpose of this article is to communicate comprehensive information to healthcare providers about methadone as a medication, and the treatment guidelines of maintenance programs in the hopes of diminishing the stigma attached to methadone maintenance therapy. Through a comprehensive literature review, information regarding mechanism of action, maintenance therapy program guidelines, different barriers to treatment, and how to overcome these barriers were collected and reviewed.
Read More →
A Valuable Lesson on Loss
I account a patient experience where I learned lessons on loss, independence, and not passing judgements.
Read More →
A Purpose
In 1st grade I lost my best friend to Leukemia, which made me realize I wanted to be a nurse. I want to specialize in pediatric oncology because my cousin touched my life even at a young age.
Read More →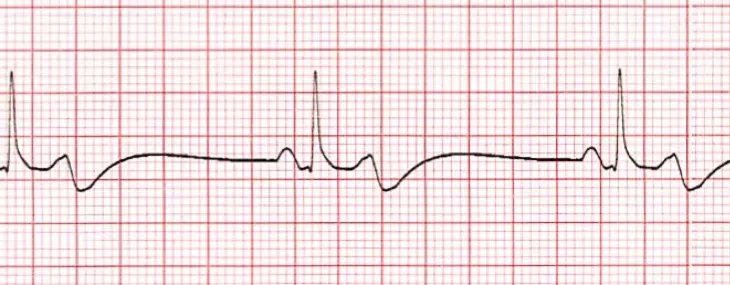
Medication Induced Bradycardia
In medicine there is never a playbook about how things are going to unfold and this is especially true when it comes to recovering from surgery and anesthesia. For example, sometimes as nurses we give medications to treat one symptom and unintentionally cause another.
Read More →
History of Ebola and Nursing
Many healthcare providers and the public are paying very special attention to the outbreak of the Ebola Virus in West Africa and the subsequent infection of the two critical care nurses at Texas. Many healthcare professionals expressed their confusion about the virus and the seeming stigmatization of nurses. Currently with the outbreak in Texas, nurses and other healthcare providers were encountered the same dilemmas as Central Africa nurses years ago.
Read More →
Psychological Factors Affecting Eating Habits Among Nurses in General Hospitals
Obesity and overweight are more frequent in workers working in shift and psychological distress increased among working women in Malaysia. A supportive manager and a flexible working time are linked with a decrease of the conflicts between family and work. The purpose of the research was to investigate the patterns of eating habit and its relationship factors, with focus on psychological factor among nurses. A study of 100 nurses was conducted in medical-surgical wards of a public hospital. Data was collected using a cross sectional study using a convenience sampling (non probability). A self-administered questionnaire on eating habits was used, and analyzed using SPSS (version 21). Results: A majority of (89%) participants was from a female group while a number of male participants are only (11%). Majority (86%) responded they ate because of feeling happy followed by eating because of feeling lonely (80%) and most of them did not perceived that they have a healthy eating habits (53%). Conclusions: The findings indicated that employers need to identify physical workload that is acceptable to avoid risks of unhealthy eating habits and monitor the availability of healthy food in the worksite. Keywords: Eating habits,Psychological Factors, working in shifts.
Read More →
Clinical Considerations for Patients with Active Clostridium difficile Infection
This article addresses the probable significant environmental Clostridium difficile (c. difficile) spore contamination that occurs when patients with active C. difficile infection are utilizing low air loss mattress therapy. We site published works that have proven environmental contamination exists in the absence of low air loss therapy. We assert that by virtue of the mechanism of action of low air loss surfaces, significantly increased environmental soiling is inevitable. Therefore, the risk of spreading infection is significantly increased. We are calling for additional research to determine the extent of increased contamination that occurs when low air low therapy is used on patients with active C difficile infection.
Read More →
"Phase 1; Exploration of paramedic protocol for field IV insertion" and "Field IVs: To Replace or Not"
Current protocol at a south central hospital in the U.S. requires nurses to change field IVs within 24-48 hours. Changing IVs in-hospital result in patient duress and nurse time loss. This article reports data from the IV Insertion Protocol Survey and the Paramedic Educator Survey. These surveys attempt to identify paramedic protocol and practice related to IV insertion and aseptic technique. Further, the surveys explore paramedic education regarding IV insertion.
Read More →
What Role does Cultural Diversity play in Patient Safety?
Cultural Diversity plays a very important role and will continue to play an even greater role as we move into a more diversified world. We live in an era of constant change and transformation, which in return paves the way for cultural transparency. The U.S. population consists of members from different racial and ethnic groups and depending on their geographical location, they can either be more or less concentrated.
Read More →
Bearers of Light - A Poem
A poem about nurses. The bearers of light in the darkness of patients' lives.
Read More →
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Insipidus (DI) is a deficiency response to the antidiuretic hormone (ADH) also known as vasopressin. There are two types of vasopressin (V) receptors known as V1 and V2 in which the V1 receptors located in the vascular smooth muscles cause vasoconstriction whereas V2 receptors located on the tubular cells of the cortical collecting duct control the reabsorption of water via the kidneys. DI effects the renal mechanisms of the water reabsorption which is particularly imperative for maintaining body fluid osmolality. Edification that medication management is available in conjunction with readily accessible liquids at all times to replenish the enormous losses that occur through urination in addition to enforcement that this disease can easily turn to life threatening if not managed properly.
Read More →

The Novice Nurse
This article is an ode to doing new things in an old profession and a guide to being funny. I work with a nurse who has been working in the same department for twenty years plus. When she is asked to do something, she often remarks, “I don’t know what the hell I am doing”.
Read More →
Rising to the Challenge of Nursing Education
As the nursing shortage and nursing faculty shortage continue, it is imperative that we look to innovative measures in order to increase the number of available baccalaureate prepared nurses. At the same time, it is crucial that we do not neglect the quality of education required to receive the Bachelor of Science in Nursing degree. This paper examines potential solutions to the ongoing nursing shortage.
Read More →
The Cost of Caring
Nurses care for individuals when they are most vulnerable and often serve as emotional outlets. It is this deep caring that can lead to nurses becoming burnt out or developing vicarious traumatization, secondary traumatic stress, or compassion fatigue. Awareness of these phenomena and methods of prevention needs to be increased throughout the profession. This includes teaching nursing students as they begin having interactions with patients in the clinical setting.
Read More →
The Birmingham VA Nursing Academy Partnership
This article describes a partnership and the importance of partnering with the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Nursing as part of a pilot program in The United States to promote nursing careers in the VA hospital and to improve the quality of nursing education in the School of Nursing. Since it began, in 2009, this program, called the Veterans Affairs Nursing Academy Partnership, has consistently performed beyond expectations to increase the breadth of knowledge for a select group of baccalaureate nursing students. Further it has created a strong connection between the Birmingham VA Medical Center and the University of Alabama at Birmingham School of Nursing, a professional resource that benefits all students and faculty.
Read More →
Managing behavior in children with ASD
Unfortunately, many of these children end up in the emergency department for these behaviors due to the lack of community mental health services. These crises visits often times result in unnecessary medications being prescribed for these problematic behaviors.
Read More →
Love in the ICU
The love I have witnessed between people during my time as an ICU nurse.
Read More →
One Day, One Shift, One Year
Nurse's experience of delivering a baby in the restroom of an ED.
Read More →
Not Just Another Day
Brief story about helping someone say goodbye and knowing their loved one was cared for.
Read More →
Sleep Deprivation of Nurses: Poor Health Care Practice
Sleep deprivation of nurses and its impact on patient care
Read More →
Embracing Change
Exemplar of my nursing experience of my transition from ER nurse to an ICU nurse.
Read More →
Self Examination of Body: An Effective Measure for Early Detection and Treatment Properly of Cancers among Girls/Women in Rural Area and Slum Area of India
Cancer is the one of the scariest and second largest non-communicable disease. It contributes a sizable in the total numbers of deaths. The World cancer Report, 2003 indicates that cancer rates are set to increase at an alarming rate globally and it would be increased by 50% new cases for the year 2020. In case of India the number is expected to rise seven million by 2015. Ignorance among the public, delayed diagnosis and lack of adequate medical facilities has given it the dubious distribution of being a ‘killer disease’. Only early diagnosis and properly treatment strategies can be prevented the one third of common cancers. It is the prime matter of concern that the female population at their reproductive age and beyond is badly infected by the disease. The incidence of breast cancer, cervix and ovarian cancer are raising steadily. There are several factors like life style and diets specially among urban women associated with this increasing rate of victimization. But among females of rural and urban slums it speaks another scenario because these female populations has a little scope of self examination of their body which is an effective strategy rather than education, awareness and screening test.
Read More →
Ubiquitous Health: An Emerging Technology in Todays World
A look into the future and the use of technology to implement ubiquitous health systems.
Read More →
True Suffering In An ICU
Essay concerning the view of various interactors in an ICU. Told from the perspective of a Professional therapeutic counselor who has counseled doctors, nurses, family, allied health and patients. Considers the suffering of all involved in the daily interactions of the ICU milieu.
Read More →
Understanding and Treating Benzodiazepine Dependence; How you as a nurse can best assist the addicted patient
This article provides information on the symptoms of benzodiazepine dependence, the neurophysiology behind the dependence and how the staff nurse can be part of the treatment involved.
Read More →
A Difficult Patient
Article about managing a difficult patient in the PACU setting. In my nursing career, there are many different types of challenges. Job challenges, schedule challenges and patient related challenges. No matter what type of nursing I have encountered there are always difficult patients that test my nursing skills. Whether the demands are related to technical skill, assessment or cultural understanding, I enjoy that critical thinking that is required to rise to the occasion. As a seasoned nurse I feel that technical challenges have become easier to handle, while the social or cultural challenges have my increased interest. I continue to obtain as much education as I can to assist my nursing challenges.
Read More →
Teach Your Children CPR
CPR is a skill most anyone including our own children can learn. It is a skill that needs to be taught in all schools. We should not underestimate our youth being able to save someone's life by performing CPR.
Read More →
Eating Disorder among Elderly Causing Heart Attack in Post Retirement Life
In the era of globalization growing elderly faces multifaceted problems range from absence of ensured and sufficient income to support themselves and their dependents, to ill-health, absence of social security, loss of social role and recognition, and non-availability of opportunities for creative use of free time in all societies of India in their post-retirement. In developed countries population ageing substantially shifted in social programmes.
Read More →
A Study To Exploring Nursing Students' Lived Experiences In Pediatric Clinical Practice In A Selected College, Chennai
The results of this research can serve as a reference for nursing teachers to design appropriate courses for pediatric nursing curriculum.
Read More →
Receiving another patient helped save my other patient...
I started my day in the Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU). I work the 7a-7p shift. It was just another routine day. I received an 84yr old female patient Mrs. R from the Main Operating Room (OR) who had undergone a Left Shoulder Replacement. Mrs. R received an interscalene block for pain in the OR and had general anesthesia. Since she was elderly and was not having good tidal volumes at the end of the case anesthesia decided to keep her on the ventilator a bit longer until she woke up more...
Read More →
Going Against the Norm: Treating Cancer as a Metabolic Disease
The current treatment for someone diagnosed with cancer is no longer acceptable. The focus needs to shift away from our standard treatments which so often causes pain as well as physical and emotional suffering. Emerging research about the body’s cellular metabolism provides new hope for cancer prevention and treatment. A number of mechanisms present in the human body are known to inhibit cancer cell growth by providing the body with an alternative fuel source, one that cancer cells cannot metabolize. For instance, induced ketosis offers a physiological means of regulating glucose metabolism in cancer patients while suppressing tumor metabolism and progression while ketone production significantly produces anti-cancer effects by shifting the body’s fuel source from a glucose dependency to one that is ketone based. Even while there remains controversy over the occurrence of many types of cancer, recent research has unveiled promising results towards cancer prevention and treatment. Emerging evidence indicates cancer is primarily a metabolic disease. According to Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (2014) research is being done to look at the connection between body weight, sugar intake, insulin levels and their correlation to cancer. Understanding the cellular metabolism of cancer is necessary in order to find preventative and holistic treatment modalities and for this to occur, a paradoxical shift in our current perception of cancer treatment is necessary.
Read More →
Distracted Driving and Young People
Distraction while driving occurs any time you take your eyes off the road, your hands off the wheel, and your mind off your primary task: driving safely. There are three main types of distractions: Manual, Visual, & Cognitive. It is this last type of distraction – known as cognitive distraction– which appears to have the biggest impact on driving behavior, especially for young drivers. Young drivers, for the purpose of this paper, will be defined as those ages 16-20. According to Distraction.gov, “young drivers are 4 times more likely than any other age group to be involved in a crash while distracted”. They are also 44% more likely to text. 73% of those surveyed report driving while texting. This results in 23 times more likelihood of crashing. In fact, 16% of all distracted driving crashes involve drivers under 20. Crashes are the leading cause of death worldwide among those aged 15–29 years.
Read More →
Understanding behaviors in Autism Spectrum Disorder
With the rising incidence of Autism Spectrum Disorders, nurses need to be educated regarding comorbidities that can cause aberrant behaviors. Along with a thorough medical assesment, finding mental health services can be challenging for many families. Many PCP's and other non-mental health professionals take on medication management of behaviors due to the lack of appropriate mental health resources.
Read More →
Post-Operative pain management in Total Joint Replacements: Finding a Balance
Post-operative pain can place patients at high risk for complications.
Read More →
Authentic Leadership in Nursing
Authentic leadership, I choose this topic because it is what I aspire to be. I was treading on serious unfamiliar territory. I have never ventured upon this characteristic, but none the less; I want to be an authentic leader. I have been in the nursing world for over 20 years and have never met this strange and unfamiliar character called the quintessential “authentic leader”. I have worked with many different mangers in my career. I have noticed a common thread with each one .Leaders that were daily, dealing with emotional upheavals trying to balance their career and families. The stress from this unhappy medium; lead to mood swings and attitudes when they had a bad day. I remember as a staff nurse hiding behind curtains in my patient’s rooms to avoid the emotional outburst of my managers. This role of a leader all seemed frightening to me. I often wonder how this person is making a difference in patient care with such high levels of stress. I never had a good role model of a leader. But as I read the literature about authentic nursing leadership my spirit leaped and I could truly identify with the characteristics of this type of leader. This type of leader ventures out and takes risks and has a goal to exceed the standards of care; and is a trailblazer in the field of nursing. Authentic nursing leadership is multifaceted.
Read More →
Clinical Decision Support Need for Standardization
Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) is interactive software that assists physicians in decision-making about their patients. The system utilize data from pharmacy, laboratory, radiology, and other patient monitoring systems to help physicians in enhancing patient care. Statistics show an increase in the number of medical institutions adopting CDSS in pursuit of reducing errors, improving the nursing documentation and improving patient outcomes. This paper discusses errors arising from the use of CDSS and ways of preventing them.
Read More →
Educational Requirements for Baccalaureate Nursing Faculty: How do the States Differ?
Nursing shortages have plagued the United States for the past several decades. By 2020, the deficit of Registered Nurses (RN) is projected to exceed 1.2 million (AACN, 2012). One important factor is the shortage of qualified nursing faculty. Every year many qualified applicants are denied admission to nursing programs due to nursing faculty shortages (AACN, 2012). Nursing programs can only accommodate as many students as they have faculty to teach. State Boards of Nursing (SBN) throughout the country are collaborating with colleges and universities to fill nursing faculty vacancies utilizing a variety of creative strategies. An educational research team, at a private university in the Midwestern section of the country, examined each state’s SBN rules and regulations related to pre-licensure faculty requirements for baccalaureate nurse educators. The researchers found that there were vast differences in the educational requirements allowed by individual State Boards of Nursing for Baccalaureate nurse educators.
Read More →
The Hospital Room: Not Just Four Walls
The patient room is a place where patients and families learn about an illness and treatment plan, and where patients get better or worse. It is very important for nurses/nursing students to get a sense of the emotion that goes on in these rooms, the room is more than four walls.
Read More →
Advocacy for Those without a Voice: Helping Parents with Smoking Cessation
The purpose of this manuscript is to summarize current research in the area of second-hand smoke exposure in children and smoking cessation interventions for their parents.
Read More →
Women's knowledge regarding preventive measures of Food Poisoning in Khartoum, Sudan
The objective of this article is to assess the mothers' knowledge regarding preventive measures of food poisoning in Khartoum. This is a descriptive, cross-sectional study; it was conducted in Alemtidad area during period extended from September to December 2012, it involved 88 mothers selected by convenience. Data were collected by using designed questionnaire then analyzed by (SPSS). It was found that; mothers’ knowledge about preventive measures for food poisoning is satisfactory concerning; hand washing, washing vegetables and cooking appropriately. The economic status, level of education, and housing condition are not predicting factors influencing level of mothers’ knowledge about food poisoning. The mothers in Khartoum have acceptable level of knowledge about food poisoning. There is need for strengthening the situation through education sessions
Read More →
Dear Mr. R
If you could write a letter to that patient you just can't forget, what would you say?
Read More →
A Shout Out to New Grads: Smoking Cessation Education Today and Everyday
All nurses, especially new grads, must bring tobacco cessation education into daily pratice
Read More →
Making the Transition From Student to Working RN
Guidelines and tips for transitioning to working nurse and additional tips on surviving the first year.
Read More →
Let's get rid of the "bad apples"
One of the most stressful challenges of the nurses working environment has become working among our own colleagues. Terms such as “Incivility”, “Bullying”, and “Lateral Violence” are now included among our long list of stressful issues nurses face each and every day. These terms include behavior that is undesirable for any institution and is counterproductive in any environment. Undesirable behaviors can involve not only nurses but any employee in an institution including that administration. The effects it has on nursing can be detrimental to the entire profession and even cause many to leave the profession of nursing altogether. We must begin to address this issue with specific interventions and we must do it now for it can and will taint the image of nurses who are smiling at work, providing caring, compassion, and good rapport with their fellow colleagues and have an investment in the organization to do well.
Read More →
Remember When We Were Nursing Students
I remember, as most nurses can, their days in nursing school, feeling anxious and scared going to clinical rotations to take care of real living patients and not just the mannequins in the lab. Most us can also recall how the floor nurses treated us as students engrossed in our clinical rotations. There were nurses who made a positive impression on us and unfortunately there were nurses who did not make a positive impression. Terms such as “Incivility”, “Bullying”, “Vertical Violence” and “Internal Violence” have become too familiar in today’s nursing literature. As an Associate Professor of Nursing, it is a shame to have to include such terms in nursing lectures and worse of all trying to explain reasons this may be happening among nurses and just may happen to them as nursing students. According to Luparell (2011) “Because today’s student are tomorrow’s colleagues, conversations regarding incivility and bullying should include specific aspects of nursing academia and the preparation of new nurses”.
Read More →
No, Ms. Ray, I am not lucky to have a job!
Response to HR telling nurses they are lucky they have a job after cutting pay and benefits.
Read More →
The Cardiac Diagnostic Interventional Symposium (CDIS)
The symposium focused on nursing and allied healthcare professional education.
Read More →
Response to "I Quit My Nursing Job Yesterday"
I have attempted to respond to an article written by Linda Ritter called "I quit my RN Job yesterday". It is a very moving article and wanted to give her my input an overall situation.
Read More →
A Thank You to Nurses
A brief look into the daily trials and joys of the intensive care unit.
Read More →
Mental Health Need Assessment Tool
Patient assessment is the first step in the nursing process. Assessing for mental illness is necessary in order to provide safe and competent care. Using a tool that incorporates Maslow's hierarchy of needs to assess if a patient feels that their needs are being met or not met is a good first step to begin assessing the mental health status of our patients.
Read More →
It Is Time to Openly Assess & Discuss Mental Illness
With the prevalence of mental illness on the rise, nurses in all healthcare settings are going to be tasked with providing care for patients with a mental disorder. Thus, it is necessary to provide nurses with the skills necessary to care for patients with mental illness.
Read More →

What do they expect? A comparison of student expectations and outcomes of undergraduate research experiences
The big challenges facing nursing students today have permanent effects on us all as patients. Nursing students need to be able to value the relevance, authority, and utility of nursing research for patient care through embedding research learning in both academic and practice-based settings. Students can be supported in learning how to access, understand, and appraise the authority of research through weaving these skills into enquiry-based learning. Furthermore, encouraging students to undertake research- based practice change projects can support research utilization and development skills.
Read More →
Our Responsibility at Tech-Savvy Nurses
With the advent of electronic charting in the workplace comes new challenges for nurses and medical professionals. As computer users, we can help make the transition easier for those nurses, nursing assistants and nursing students who are not as comfortable with technology. This article lists a few ways to do so.
Read More →
Effectiveness of Sexual Health Promotion in Adolescents
The authors illustrate the importance of sexual health promotion in the adolescent population through school-wide and community based efforts through a literature review composed of peer-reviewed, primary sources.
Read More →
Cortical Dynamics as a Therapeutic Mechanism for Touch Healing
Touch Healing (TH) therapies, defined here as treatments whose primary route of administration is tactile contact and/or active guiding of somatic attention, are ubiquitous across cultures. Despite increasing integration of TH into mainstream medicine through therapies such as Reiki, Therapeutic Touch,™ and somatically focused meditation practices such as Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction, relatively little is known about potential underlying mechanisms. Here, we present a neuroscientific explanation for the prevalence and effectiveness of TH therapies for relieving chronic pain. We begin with a cross-cultural review of several different types of TH treatments and identify common characteristics, including: light tactile contact and/or a somatosensory attention directed toward the body, a behaviorally relevant context, a relaxed context and repeated treatment sessions. These cardinal features are also key elements of established mechanisms of neural plasticity in somatosensory cortical maps, suggesting that sensory reorganization is a mechanism for the healing observed. Consideration of the potential health benefits of meditation practice specifically suggests that these practices provide training in the regulation of neural and perceptual dynamics that provide ongoing resistance to the development of maladaptive somatic representations. This model provides several direct predictions for investigating ways that TH may induce cortical plasticity and dynamics in pain remediation.
Read More →
Effect of Evidence-Based Method Clinical Education on Patients Care Quality and Their Satisfaction
Nowadays, evidence-based education with a serious purpose, explicit and rational than the best current evidence to decision-making in nursing education has been addressed. This study aimed to assess the effect of clinical evidence based on the quality of patient care was performed Usual care based on traditional evidence-based care training has been under almost identical. Student feedback questionnaire data, patient satisfaction and quality of care were collected and then were analyzed with descriptive and inferential statistics. This study suggests that the use of evidence-based education in nursing care is not only effective as traditional education. But also knowledge and skills and promote high quality of care and the patient's hospital stay and costs were reduced.
Read More →
The Far Reaching Impact of a Child
Emergency care of pediatric patients leaves a deep impact to nurses career and lives. When these young lives are altered or end, how is the profession caring for the nurses left behind. This article explores the need for awareness and support during these trying times to return the nurse back to wellness.
Read More →
Alternative Treatments: Doubting Thomas to Believer
My experience with reiki therapy and how it forever changed my practice.
Read More →
Nurses And IELTS Exam
IELTS has been a fast growing organization over the years. I think It's expensive and it shouldn't be a requirement for nurses who want to work abroad. After all, most nurses know how to write, read, speak, and understand English.
Read More →
Care of the Pediatric Patient
Short exemplar about caring for a pediatric patient in Interventional Radiology
Read More →
Foley Catheters in Men and Women: Lubrication, Anesthesia, and Attitude: A Randomized Trial
Foley insertion in alert patients not in retention: males benefit from lidocaine jelly. All staff appear to underestimate discomfort.
Read More →
Applying Ethical Standards to the Assessment of Pain
A nurse's role and responsibility is to ensure that our patient(s) receive adequate care and our assessments are comprehensive and thorough. One of the methods of assisting with pain assessment is applying ethical standards.
Read More →
Seconds Of Safety Port Angeles, S.O.S. PA
In response to the need for hand hygiene education the second year nursing students of Peninsula College created a campaign centered around the W.H.O. guidelines for the citizens and healthcare workers of Clallam County, Washington. The project received positive response from Olympic Medical Center and other local area businesses and was featured in multiple local publications.
Read More →
Hurray for the Millennial Nurses!
This article discusses horizontal violence in the field of nursing and how we as educators can provide them with the skills to create a more civil work environment.
Read More →
Early versus Later Rhythm Analysis in Patients with Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: A Quantitative Critique
The critique of the study Early versus Later Rhythm Analysis in Patients with Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest evaluates strengths and weaknesses in relation to the generalizability of the study. The significance of the study is assessed, as well as the literature review, purpose, hypothesis, findings, and limitations. The study provided information regarding protocols on performing CPR on out-of-hospital patients. Although the findings were not clinically or statistically significant, the study did offer useful knowledge that both methods of rhythm analysis with CPR provide similar outcomes. This study failed to provide additional knowledge on the topic. Ultimately, further research should be completed on the best treatments for out-of-hospital cardiac arrests.
Read More →

The 12 Days of Christmas: Revisited for Nurses
A comedic take on the classic Christmas song from an Obstetric Nurse's point of view.
Read More →
Do We Really Know Who Our Patients Are?
The profession of nursing has become so task orientated that we often forget to ask, "Who is our patient? ”What was their life like prior to becoming ill?" With advances in technology and the business atmosphere of healthcare nurses are often not able to provide patients with one of the most fundamental core competencies of nursing, caring.
Read More →
Cardiac Amyloidosis: The oft times missed cardiomyopathy - A nurse's personal story
Having been in nursing for over 30 years, nothing I had learned in school or through experience would prepare me for the long, misdiagnosed disease my husband suffered that eventually took his life. Forever changing my perspective on healthcare, it has prompted me to share this story with other nurses, hopefully, averting this course for other patients, and possibly one’s own family member.
Read More →

LASIK eye surgery - Will you want your glasses back?
This is an article I wrote for a Ethics of Health Policy class in the nurse practitioner program I am presently a part of offered by Indiana Wesleyan University.
Read More →
Terminal Illness
Doctors and nurses are faced everyday with the ethical dilemma of telling their patients that they have a terminal illness that they will soon die from. How do we as healthcare professionals address this situation?
Read More →
Asymptomatic Bacteriuria: The Question for Treatment
To improve the quality of care in patients with asymptomatic bacteriuria to promote safety.
Read More →
Euthanasia, Assisted Suicide, and Nursing
Ethical dilemma of euthanasia and assisted suicide and effect on nursing.
Read More →
Poor sleep, hazardous breathing: An overview of obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea is a chronic disorder resulting from upper airway collapse during sleep. It is linked to a variety of health and safety risks but can often be effectively treated. This article provides an overview of the disorder, including an evidence-based approach to diagnosis and management.
Read More →
Be the Nurse you REALLY Want to Be
When asked for my advice I encourage them to be brave, take risks and aggressively pursue your professional dreams. Too many new nurses say they won’t apply to the specialty the long for because they don’t thing they have enough experience. I really feel like this is highly self-limiting. In this field the knowledge and experience never ends. You won’t get every job you want but you have nothing to lose by trying. If your dream is to become a trauma nurse and you work in a nursing home it’s time to take action. Nurses generally know far more than they give themselves credit for. Begin to really evaluate your skills and give yourself credit for what you know the experiences you have, and don’t forget about the non-nursing experiences as well.
Read More →
Health and Law
This legal case study involves a young woman who presented ambulatory to the emergency room with a gunshot wound to the head.
Read More →
National Nursing Licensure
National nursing licensure promotes more effective licensing than does state licensure by alleviating the ever-present nursing shortage and promoting mobility among the nursing workforce.
Read More →
Elective Induction of Labor and Early Term Delivery
The rate of elective induction of labor without medical indication is on the rise. Elective inductions carry long-term consequences for the maternal and infant dyad. Maternal risk of induction includes hemorrhage, uterine dystocia, uterine rupture, and cesarean section related to failed induction of labor. Neonatal risks include respiratory distress, feeding difficulty, and long-term psychological and behavioral tendencies such as attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). In reviewing a variety of studies, researchers have seen a decrease in morbidities and health care costs for both mother and infant when spontaneous labor occurs. However, the risks of liability and malpractice suits tempt physicians to schedule elective inductions. By creating and implementing policies on elective induction of labor, nurses have the ability to educate patients on the importance of letting labor occur naturally.
Read More →
Managing Type II Diabetes within the Hispanic Community
Diabetes is termed the life style disease for good reason. It is a progressive and chronic illness largely caused by obesity and lack of exercise. If left untreated or poorly controlled, this disease can lead to debilitating complications and premature death.
Read More →
Professional Nursing: Is A Doctorate Degree Necessary?
Obtaining a higher education has transitioned from being a privilege to a prerequisite for professional success. However, success is not always correlated with the level of education the individual possesses. This is especially true in the field of nursing.
Read More →
Effects of Music Therapy in Pediatric Mental Health
Whether it is the simple melody of a lullaby to the crashing drums of rock and roll, music evokes an emotion in all of its listeners. Music has been around for centuries creating an environment of healing. When working with pediatric mental health patients, pharmacological interventions are often the solution to manage symptoms and negative feelings.
Read More →
Do nurses really understand Advanced Health Care Directives?
As a Nursing Supervisor, I have witnessed many problems associated with patients Advanced Health Care Directives (AHCD). On many occasions, patients are asked about AHCD when their medical condition worsens, leaving education of AHCD lacking and often put to the family to make end-of-life decisions. Both nurses and patients have verbalized not understanding AHCD. At the local hospital not only have many nurses acknowledged not understanding their role and responsibility about AHCD, but they also do not really have a good understanding themselves of what AHCD are; therefore, they do not feel comfortable educating patients and families about this vital healthcare issue. Research shows that providing AHCD education is effective in changing not only the treatment preferences of patients, but their attitudes toward end-of-life health care (AHRQ, 2003). There was an eminent need to look into this problem at the local community hospital.
Read More →
Funding Health Care as a Basic Human Right
The United States of America is a nation known and heralded worldwide for its democracy, freedom, and wealth. Through our commerce, we have become a prosperous nation. Through our commonalities we stand united. Through our shared citizenship, we establish our community. Through our voices, we are heard. So why is it, our nation has been divided against the idea of health care being funded as a basic human right? U.S. Senator, Ted Kennedy, once said,
Read More →
Literature Review: Safe Nurse Staffing
The purpose of this literature review is to exam nurse staffing and staffing related issue and its impact on the healthcare world. Safe nurse staffing poses substantial issues at the clinical level including its tremendous impact on patient mortality, patient satisfaction, increased incidence of medical errors, and nurse dissatisfaction and burnout.
Read More →
Doing More with Less: Are We Compromising Patient Care?
I came bustling into the Medical-Surgical unit at the hospital where I work as scheduled. It was the third 12-hour shift I was working, so I was really looking forward to getting the shift over with and enjoying the upcoming four days off. I was expecting to come onto the floor to find the usual nurses on the unit.
Read More →
Moral Distress in Nursing and Available Support Systems
Moral distress is a key issue facing nursing today; it affects the way nurses care for their patients and the number of nurses who stay in the profession (Gutierrez, 2005; Hamric & Blackhall, 2007).
Read More →
Multidisciplinary Rounds In Various Hospital Settings
This paper focuses on the use of multidisciplinary rounds in various hospital settings with an emphasis on intensive care units. A comprehensive literature review on the studies that focused on the use of multidisciplinary rounds will be incorporated and referenced. Topics to be discussed in regard to application of multidisciplinary rounds are benefits, barriers, gaps in current literature, and recommendations for baccalaureate level nursing.
Read More →
"What is it with you?"
“I’ve got a fainter here!” I call over my sister’s head to the flight attendant. My sister is sitting in the aisle seat, I am in the middle, and my new patient is sitting by the window. He has just announced to me that he doesn’t feel well and thinks he may faint
Read More →
Basics on Inpatient Blood Sugar Control
Controlling inpatient blood sugars is challenging and complex. Inpatient blood sugars can be affected by a multitude a variables. Some of the variables are nutritional intake, inflammation, stress and steroids. Research indicates more than 50% of Americans could have diabetes or pre-diabetes by the year 2020. Healthcare costs for this population both inpatient and outpatient is enormous and growing. Many of these patients will require hospitalization. Inpatient diabetes treatment can be complex but the outcome enhancement is great. Improving inpatient blood sugar control decreases both complications and mortality. Controlling the blood sugars of this growing patient population is well worth the investment of time and resources.
Read More →
Health Promotion and Disease Prevention
The United States falls behind in healthy outcomes when compared to other countries.
Read More →
Implication of Foreign-Educated Nurses on United States Nursing Collegiality
The United States (U.S.) has repeatedly experienced a shortage of qualified registered nurses, a situation, which is capable of deteriorating further in view of the U.S. aging population (Clark, Stewart, & Clark, 2006).
Read More →
Nurse/Patient Communication Twenty Suggestions for Improvement
From time to time, physicians are taken to task by fellow physicians and many others for a variety of shortcomings in the practice of their profession. Common among the listed faults is a lack of effective communication with their patients.
Read More →
Electronic Medical Record: How its Use Facilitated an Increase in the Number of Patients with Diabetes to Achieve the Target Measurement of Having at Least 2 HbA1c Tests Performed in a 12 Month Period.
We are in the midst of an unprecedented era, the convergence of technology and medicine. Even stories of failures are not true failures because of all we stand to learn from the experience of others. Technology has enabled those in the field of medicine to move forward with their own improvement projects
Read More →
Stem Cell Research is Our Future of Cures
People have the power to change the world. The donation embryos are a step in the right direction for resources to continue research to help society in the future. It is not the intent to clone but to cure. Life is a gift that we should keep giving with this great opportunity.
Read More →
The Reality of Diabetes in Rural Mexico: A Nursing Student Perspective
Students from six universities in Canada, Mexico, and the USA participated in a service learning exchange. In order to understand the needs of diabetes patients in rural Mexico three students from Canada and the USA trudged in the heat through the rough terrain to their homes. We used Omaha System signs/symptoms to collect interview data. The standardized language of the questionnaire allowed us to be aware of the interaction between traditional medical beliefs and the western medical model. Some of these challenges include maintaining the traditional family roles, controlling blood glucose levels without the appropriate medical equipment, and economic barriers. One patient was responsible for both caring for her eight young children and working in the fields to put food on the table. Additionally, she was in a constant hypoglycemic state causing her to faint in the fields. We also visited a visually impaired man that was distraught because he needed to rely on others for help in a machismo society. He said “While living in New York City, I was a victim of a robbery. I was so afraid because I thought I was going to die and as a result I got diabetes.” Though some may find this comment strange, it is a common theory among the rural population in Mexico. We will always remember the many Mexican speculate that eating bread absorbs the scare and thus prevents diabetes. This experience gave us a glimpse of the harsh reality that these people face everyday coping with diabetes.
Read More →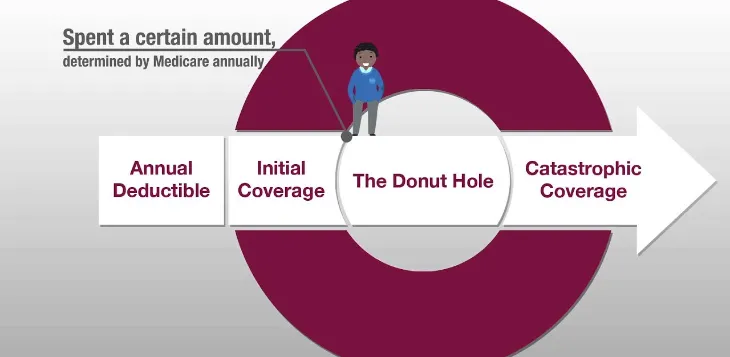
Closing the Donut Hole: Who Will Pay?
The dark black hole in the Medicare Part-D prescription plan called the donut hole is finding the light, or is it? Health care reform has promised to close the donut hole for Medicare recipients completely by the year 2020 (Gionfriddo, 2010). The Consumer Report on Health (2012) confirms medication costs continue to rise with no end in sight. Who will pay the gap between what is currently covered and the predicted added coverage with Health Care Reform? According to the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS, 2011) the Medicare trust fund is currently running in a deficit. Reducing the burden of our Medicare population, with associated out-of-pocket expenses for prescription drugs, cannot be achieved by a system already running in a deficit. As we start to unravel the mystery behind closing the donut hole, can we identify who will pay?
Read More →
My Professional Path as a Nurse
When I was a little girl, I’ve always been fascinated to see nurses in white uniform. I have this inner desire that nursing is something that I really wanted to do. Eventually, I enrolled in the nursing program and finished my degree. I started working in medical area and I learned that to be a nurse you have to be caring, patient, integrity, intelligent, have a compassionate and listening ear, and always seek knowledge for advancement.
Read More →
Withdrawal in the Pediatric Cardiac Population
Oftentimes patients admitted to the Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit are placed on narcotic and/or benzodiazepine intravenous infusions after surgery, especially if prolonged intubation is expected. It is generally assumed that after a period of 5 days on continuous infusions or administration of around the clock opioid/benzodiazepine administration, the patient should be monitored for signs of withdrawal.
Read More →
Promoting the Sexual Health of Older People
This paper examines the issue of sexual health and older people. It identifies sexual health in this population group as a component of health that is often overlooked. As a practitioner of Gerontological Nursing, the author seeks to determine why this is and what can be done about promoting sexual health for this population group. Initially health promotion and sexuality are defined before outlining the rationale for the choice of this topic. Incorporated into the discussion is the acknowledgement that this is an area requiring significant development for all older people, regardless of sexual orientation, that in fact the need for health promotion for older gay and lesbian people may be a more pressing issue overall. Having outlined the need for health promotion, a number of strategies are introduced. Relatively little research into this specific issue has been conducted thus health promotion strategies in more broad terms are discussed.
Read More →
FNP Student Assessment of Acute Abdominal Pain
This article serves to assist the novice family nurse practitioner student in the examination of abdomen in a patient presenting with acute abdominal pain.
Read More →
The Blessing: A Nurse's Story
It was nine o’clock pm and I was walking briskly out of Recovery Room, knowing I had to be back the next day at six am. Though in a hurry, I purveyed the family waiting room to see if there were any visitors who needed help after the patient representative had gone home. I immediately noticed a lone woman with an anxious look on her face. As it turned out, her daughter-in-law had just been transferred to Intensive Care. Instead of waiting for one of our transporters, I decided to take her up myself. As we headed down the hall, she stated: “I bet you’re trying to leave, aren’t you?” I affirmed her observation. I added that, it was quite all right. We arrived at the particular ICU where her daughter-in-law was transferred, and upon talking with the patient’s RN, I was able to let her in right away. She turned to me and said: “Thank you; you will be blessed.”
Read More →
Healthy Cooking for the Soul
The purpose of this pilot study was to use motivation and coaching strategies to encourage Detroit African-American adults who are at high risk for hypertension and diabetes to change their dietary patterns. Oakland University Accelerated BSN (ABSN) student nurses designed and implemented the project to bring health coaching to the urban Indian Village community. Interventions included nutrition presentations and healthy soul-food cooking demonstrations. Information about program effectiveness was obtained through surveys. Survey scores increased for ninety percent of the participants from pre to posttest, indicating a corresponding increase in nutrition awareness. Future research is needed to determine the long-term effectiveness of the intervention strategies. The Healthy Cooking pilot project has the potential to facilitate research that will educate nursing students as well as citizens of Detroit's Indian Village.
Read More →
Sally's Eyes
She was only 36 years old but Sally was dying. She spent a lot of her life in the hospital which lead her to have a complicated medical and surgical history. This hospital admission had already been five months long when I came along.
Read More →
Spinal Block versus Epidural Block
Spinal anesthesia, also called spinal analgesia, sub-arachnoid block (SAB) or intrathecal, is a form of regional anesthesia involving an injection of a local anesthetic into the cerebral spinal fluid with a fine needle. The term epidural is often short for epidural anesthesia, a form of regional anesthesia involving injection of drugs through a catheter placed into the epidural space. The injection can cause both a loss of sensation (anesthesia) and a loss of pain (analgesia), by blocking the transmission of signals through nerves in or near the spinal cord.
Read More →
Reducing Lateral Violence: A humanistic educational approach
We’ve all witnessed it: the gossip, backbiting, and bullying that too often occurs in the nursing workplace. Lateral violence (LV), also known as horizontal violence or workplace bullying, consists of behaviors including “bullying, intimidation, sarcasm, back-stabbing, criticism, exclusion, and various forms of unequal treatment”. LV has been a topic of ongoing topic of concern in nursing for many years and is particularly prevalent in female dominated professions. LV is often attributed to oppression theory, which states that nurses are an oppressed group because they are deemed less important than others (such as medical practitioners); therefore, nurses often lack autonomy and control over their profession which results in powerlessness and displaced aggression towards other nurses.
Read More →
A Needed Change in Nursing
National nursing licensure promotes more effective licensing than does state licensure by alleviating the ever-present nursing shortage and promoting mobility among the nursing workforce. Some of the many benefits of a national nursing licensure include improved patient access to quality nursing care, enhanced discipline and information sharing among the states, physical and electronic provision of care by competent nurses, and convenience of employers to more mobile and competent nurses.
Read More →
Minimally Invasive Aortic Valve Replacement
This paper will compare minimally invasive aortic valve replacement surgery and the traditional approach. This paper will discuss how the aortic valve works and different disorders of the aortic valve. The paper will also discuss the benefits of minimally invasive aortic valve replacement and complications of aortic valve replacement. Another topic covered in this paper is the anatomy of aortic valve and how the aortic valve replacement is performed.
Read More →
American Association of Critical-Care Nurses Brings its National Nurse Leadership Skill-building Program to Texas
The American Association of Critical-Care Nurses (AACN) expands its hospital-based nurse leadership and innovation training program to a fourth region with the addition of eight Austin-area hospitals. AACN Clinical Scene Investigator (CSI) Academy is designed to empower bedside nurses as clinician leaders and change agents whose initiatives measurably improve the quality of patient care with bottom-line impact to the hospital.
Read More →
Predicting exercise adherence in cancer patients and survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of motivational and behavioural factors
Cancer patients are advised to participate in daily exercise. Whether they comply with the recommendations for physical activity or not remains unclear. The review identified that both the TPB and the TTM frameworks include aspects that predicts exercise adherence in cancer patients, and thus contributes to the understanding of motivational factors of change in exercise behaviour in cancer populations. However, the strengths of predictions were relatively weak. More research is needed to identify predictors of greater importance.
Read More →
Influenza: Expert Advice You Need Now
Among other advice for managing an influx of patients with possible flu, Dr. Whitley describes his experiences with clinical decisions such as which patients should be hospitalized and who can be safely managed at home during the ongoing influenza season. He also addresses the important issue of antiviral treatment and why he believes it is an essential component in the fight against influenza.
Read More →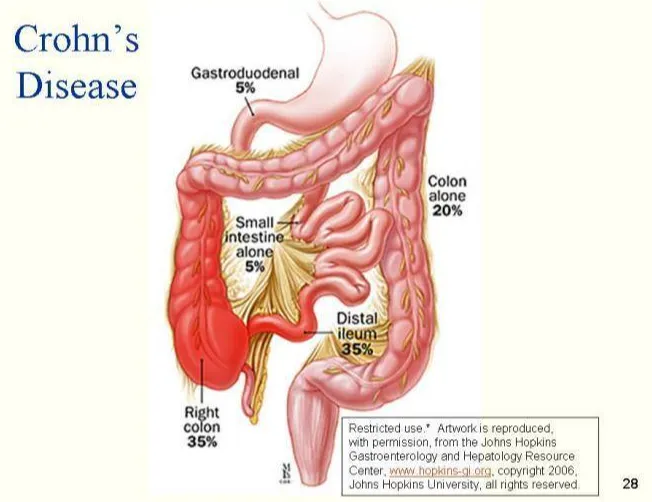
The Management of Crohn's Disease in Adults and Young People
The guideline offers best practice advice on the care of adults, children and young people with Crohn's disease. These are the first evidence-based clinical and cost-effectiveness guidelines for Crohn's disease in the United Kingdom.
Read More →
A Comet in Siberia: Kate Marsden's epic journey to the outcast Yakut lepers
A brief glimpse of the causes and effects of the remarkable journey of the British Nurse Kate Marsden into Siberia in 1891.
Read More →
A Lesson Learned
I wanted to say something brilliant. I wanted to make it better. I had nothing to say. Instead, I put my arms around this tiny woman and I held her close. Her head rested on my shoulder as she sobbed for her losses. In that moment in time, there were no call lights, no medications, and no other important matters. There was no longer any urgency as I held this woman.
Read More →
A Man Apart
The idea of individuals with developmental disabilities becoming sexually active was disconcerting. Imagine having a daughter with disabilities, with limited cognitive comprehension, how could you protect her from tragic sexual encounters? Past abuses were common as institutionalized women were sterilized without consideration of their basic human rights.
Read More →
A Mouthful of Death: Acetaminophen Overdose
In the United States, attempted suicide accounts for more than two thirds of acetaminophen-related liver injuries, whereas accidental overdoses account for only one third of the cases.
Read More →
A Rise of Syphilis in Niagara County
Sexual behavior patterns of some who are infected with Syphilis make it likely that their sexual partners will become infected, and that in turn the sexual partners of their partners will also become infected, with ever-increasing spread.
Read More →
Acute Renal Failure
Acute renal failure (ARF) has become increasingly common in patients with critical illnesses. Up to two-thirds of intensive care unit (ICU) patients develop ARF with the leading cause being sepsis. Treatment of ARF has been associated with higher costs and the following adverse outcomes: increased length of stay, excess mortality of 30-71%, need for chronic dialysis in the patients who survive, and the requirement of discharge to short-term or long-term care facilities.
Read More →

An Outstanding Journey of a British Nurse to the Yakut Lepers in Siberia
A short survey of the epic expedition into the depths of the Siberian Taiga in 1891 made by Kate Marsden, a British Nurse devoted her life to alleviating sufferings of lepers round the world.
Read More →
Are Changing Demographics Influencing the Trend of Nursing Curricula in Massachusetts BSN Programs?
An RN Journal article -a nursing student was interested to know why, with the rapidly growing population of older Americans, there was not a stand alone course related to the care of the geriatric patient offered within her SON curriculum. What were the barriers that failed to allow a stand-alone course for geriatrics?
Read More →
Evaluation of Impairment from the Kidneys: Background of Assessment for the Registered Nurse and the Clinical Practitioner
The evaluation of impairment from the kidneys, as with the findings of proteinuria or an increased serum creatinine concentration, may be your first premises in the investigation pending diagnose. In addition, rushing to a conclusion can present as a variety of clinical syndromes. In other instances, the presentation may reflect the impact of impaired renal function on other organ systems, such as edema or shortness of breath resulting from renal salt retention.
Read More →
Basic Cardiac Assessments: Physical Examination, Electrocardiography, and Chest Radiography
The human heart is one of the major organs adversely affected by high blood pressure. Therefore, the registered nurse must provide a careful and thorough evaluation of the assessments needed via the cardiac structure and function (i.e., including visual signs, all non-and invasive cardiac medical devices), which is an obligatory part of the examination of the hypertensive patient.
Read More →
Caregiver Role Strain due to Bipolar Disorder in Children
Bipolar Disorder article about the Caregiver's role and the family dynamics associated with the disease.
Read More →
Challenges in Nursing Informatics
As the use of technology explodes into the health care industry, its effects have the potential to become destructive elements to the nursing profession. This paper will discuss the evolution of nursing documentation, the immergence of health information technology, and the challenges it creates for the nursing profession.
Read More →
Change for the Best
There have been many changes in nursing in the almost thirty years since I graduated.
Read More →
Clinical Nurse Leadership and Performance Improvement on Surgical Unit
There are many ways that nurses can prevent harm to their patients one method is to provide the necessary care that will promote only positive outcomes for their patients.
Read More →
Clinical Nursing: Keeping Your Skills In-Tune
The primary duty of every nurse is the assessment of a patient’s physical and emotional well-being. This basic-skill learned in the very first nursing class is the one skill and primary duty the nurse will use every day with his and/or her patients.
Read More →
Clinical Profiling: Natural History of Essential Hypertension
Hypertension is a major cardiovascular risk factor that directly contributes to myocardial episodes such as abnormal wall motion, hypertrophies, and subsequently an infarction (MI). Also noted, are cerebrovascular accidents (CVA), congestive heart failure (CHF), peripheral arterial insufficiency (PAI), and premature mortality. Optimal and cost-effective management of the condition depends on careful diagnosis, treatment minimization, and optimized adherence to the selections of tests and treatment plans.
Read More →
Conducting Nursing Research
Evidence-based research by nursing professionals has played a major role in the advances of medical technology.
Read More →

Culturally Competent Nursing in Homecare
Homecare nurses must be culturally aware in order to appropriately care for homecare patients. Culture plays a part in the care of all types of patients but it plays a more important role in homecare. The care is being completed in the home where the patient controls the care. The nurse has to assess the cultural background of the patient in order to implement an appropriate plan of care.
Read More →
Getting a Foothold in the Nephronic Syndrome: Dietary Adjustments for the Chronic Hypertensive Type two Diabetic-Nephropathy Patients
Moderate and/or severe protein restrictions may indeed, be proposed in chronic renal failure both to fight its symptoms and to slow its progression. In diabetic patients, whether insulin-dependent or non-insulin-dependent, have a chronic disease that has generally existed for a number of years before the onset of renal failure.
Read More →
Distress and Depression Among Bone and Marrow Transplant Patients
Bone and Marrow Transplant (BMT) is a five step treatment process: screening, collecting, conditioning, infusion, and engraftment. Bone and marrow transplant treatment is very aggressive that creates significant physical, social, psychological, and emotional stress. During the treatment process, many BMT recipients experience and display a wide array of psychosocial disorders including distress, anxiety, and depression. The way an individual experiences and copes with the distress, anxiety, and depression contributes to the physiological, psychological, and psychosocial outcomes of BMT treatment.
Read More →
Exploring Communication Technology In the Family Birthing Center
Technology is being used increasingly in the health care field in order to improve patient outcomes. An e-health nursing initiative has been set forth by the Canadian Nurses Association to direct the development of information and communication initiatives. Registered Nurses’ Association of Ontario (2009) defines e-health as, "The leveraging of information and communication technology to enhance professional practice in order to promote and facilitate the health and well-being of individuals and families.” The purpose of the article is to explore ways in which communication technology in particular can aid nurses in providing more effective care, and allow for an enhanced health outcome.
Read More →
Family Presence During CPR in the Emergency Department
A descriptive survey conducted in 2000 (Myers, et al 2000) investigated attitudes and beliefs of patients’ families and ER staff members about FWR. The survey reported that 98% of patients’ families indicated that they had a right to be present and would do it and would participate in FWR again; 100% of family members said that FWR was helpful to them, and 95% said it was helpful for the patient. It also showed that 70% of professionals surveyed after their participation in FWR actually produced a higher level of “professional” behavior along with a more “professional” bedside dialog amongst the health care team. The survey also indicated that having the family in the resuscitation room prompted the staff to take the patient’s dignity, privacy, and need for pain management into greater consideration when compared to an un-witnessed resuscitation effort. (Myers, et al 2000)
Read More →
First Day of Kindergarten
Camera hanging off my neck, I prance from my car toward the playground. CRASH! THUD! POW! Right in front of the drop off zone a three car accident has unfolded before my eyes. Ella's preschool teacher, Mrs. Lewis, looks at me and declares, "Go, Cara. You're the nurse."
Read More →
Hiatal Hernia Defects and the uses of Mesh Versus Human Grafts
The purpose of this Medical Research Review is to present results of current studies evaluating the postoperative results of Hiatal Hernia defects, with special emphasis on the recurrence rate and reflux after surgery comparing the use or not of mesh reinforcement.
Read More →
HIV Crisis in Africa
The human immuno-deficiency virus/acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is of pandemic magnitude. The World Health Organization has declared AIDS as a global health emergency. Awareness of the serious global impact has climaxed, taking its place with the bubonic plague of the Middle Ages. The worst is yet to come, for there are 36 million infected and 22 million deaths from this disease.
Read More →
How Personal Digital Assistants Can Increase the Quality of Nursing Care Provided in the Hospital Setting
Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs), tools that have the potential to help nurses increase the quality of care that they provide in the hospital setting.
Read More →
I Am Dedicating This Poem To All The Nurses
I was merely twenty something, When I started my career. Nursing was my dream, And now it is my fear.
Read More →
I Quit My RN Job Yesterday
Time and time again changes were thrust on us and made to sound as if they were the answers to all our problems, when, in reality, they created more problems and basically cured nothing.
Read More →
Is There Care In Health Care - A Poem
I wrote this poem after going out one day to assist a mother with her 22 year old son who had a traumatic brain injury in a 4-wheeler accident. He had a trach, feeding tube, foley cath and skin breakdown from being in a long term care facility for 2 months. The insurance company allowed me three visits to teach the mother how to care for her son.
Read More →
Keeping a Positive Outlook: My Clinical Experience as a Student Nurse
My experience in my senior year clinical preceptorship was without a doubt unique but I feel its uniqueness was in what I made of it, something every nursing student can do for themselves. If there is one lesson to gain from reading about my experiences it should be that the success of a clinical, whether a preceptorship or group experience, is entirely what the student makes of it.
Read More →
Looks Can Be Deceiving
I asked his family to step out for a moment so I could empty his JP drains. I emptied them into a basin and I noticed that they were very dark. I inspected them a little closer and I noticed it had a greenish tinge to it. Remembering what the surgeon had said about the possibility of a bowel perforation I got concerned and called the surgeon.
Read More →
Lung Cancer: A Case Study
Lung cancer is the number one cause of cancer-related death in men and the second most common in women. Lung cancer is responsible for 1.3 million deaths worldwide annually.
Read More →
Making a Difference: Recognizing the Risk of Alcohol and Benzodiazepine Use by Older Women
Substance abuse in the elderly, specifically abuse of alcohol and benzodiazepines, is much higher than most people may think. According to a recent article published by CNN, of the 25.6 million women over the age of 59, seven percent abuse alcohol and eleven percent abuse psychoactive drugs such as benzodiazepines (CNN, 1998).
Read More →
Malnutrition in the Elderly: An Unrecognized Health Issue
Malnutrition is defined as an imbalance of nutrients caused by either an excess intake of nutrients or a nutritional deficit. Malnutrition is becoming increasingly more common among the elderly population. This is a cause for concern considering malnutrition negatively affects the health of the older adult. An estimated 5-10% of elderly people living in the community setting are malnourished (Furman, 2006). About 60% of hospitalized older adults (age 65 or older) and 35-85% in long-term care facilities are experiencing malnutrition (Furman, 2006). From these statistics, malnutrition seems to be even more prevalent in hospitals and long-term care facilities, as compared to community-dwelling older adults.
Read More →
Managing Diabetic Patients on Dialysis: The Nurse and Practitioners Role in Multidisciplinary Team Essentials
The chronic state of diabetes mellitus (DM) mainly type II, is an increasingly common cause of end stage renal disease (ESRD) in all countries, accounting for 51% of dialysis patients in the U.S. and 39% in Europe. Patient survival is much worse than for non-diabetic patients, with a large proportion of patients dying within the first 3 months of dialysis (excluded from USRDS data). In North America, chronic diabetes (e.g., poorly controlled), has shown as a major cause of death associated with cardiovascular diseases. Usually the outcome is better for transplanted patients.
Read More →
Massage Therapy as Prevention
Massage can be used as an alternative to narcotics, steroid injections, and surgery, but it can also be used as a complement to allopathic medicine to speed healing and reduce pain should surgery be necessary.
Read More →
Master vs. Apprentice
It has come to my recent attention that there is a large deficit in mentoring new graduate nurses as they enter the workforce. The development of healthy working relationships for new graduate nurses is something that is overlooked. Everyone had to have that first day on the unit or in the office when they felt scared and vulnerable. I ask you now to reflect back on your first day and how you were treated.
Read More →
Maximizing Pain Relief in Pediatric Patients
Pain management is a complex issue that has become increasingly significant in the nursing profession; so much so that the assessment of pain has become known as the fifth vital sign. This issue becomes even more crucial when attempting to manage pain in pediatric patients.
Read More →
Memories from a Haitian Cholera Treatment Center
In January and February of this year I worked in Haiti with United States NDMS DMAT and ImSurt teams providing medical and surgical care to the victims of the January 12th earthquake. What I experienced during those weeks only partially prepared me for what I would experience upon my return to Haiti
Read More →
Missionary to Haiti
On January 28th I started out on the treck to head to Haiti. Living in Honduras I found myself traveling through Miami, to get to Chicago, to head out to Haiti. But, as there were few choices of air transportation to Haiti, we took whatever we could get. Upon arrival into Haiti, the first thing that hit me was the sea of humanity. This little town held 4 million people. Keeping things in perspective, I am living in a country of 7 million people – so over half of the population of Honduras resides in the city of Port-au-Prince. We drove to our camp site, Quisqueya Christian School (QCS). We immediately found a “spot” on the grass, set up our tents, and got to the business of preparing ourselves for the tasks ahead of us.
Read More →
My Father the Medicine Man
My father continues to avoid western medicine as much as he can and there is no convincing him any different. I only hope that the next key given to me will open a door where Eastern and Western medicine will compliment each other. Health care would have the best of both worlds if this would happen.
Read More →
My Nursing Career A Whole New Appreciation
Not a day goes by, without reading in the newspaper and hearing over the radio or TV about the rising rate of unemployment in our country. It is this reality that has given me a whole new appreciation for being a nurse.
Read More →

Nurse, please pray with me.
Prayer may benefit both the nurse and the patient; both may find comfort in prayer. Prayer may also help patients and their families adjust emotionally to their illness or life events and support the patients’ spiritual health.
Read More →

Nursing Summer Camp: Recruiting the Next Generation of Nurses!
This manuscript looks at providing a nursing summer camp to school aged children with the hopes of sparking interest in the profession at a young age, as well as fostering the nursing spirit in children who may be considering the profession.
Read More →
Nursing with a Movement Disorder... DYSTONIA
Oddly enough, my professional journey through medicine intersected with a personal medical condition… one that would remain undiagnosed and untreated for five years. Some doctors said that my facial tics (hemifacial spasms) and strange pains with twisting of limbs were due to stress or some hysterical "woman's disease." Yes, we're talking this century.
Read More →
Pathogen Transmission from Blood Pressure Cuffs
Decades of research has been conducted regarding the transmission of pathogens in hospitals from patient to patient, patient to staff, and staff into the community.
Read More →
Pharmaceutical Counseling
1.5 million Americans are sickened, injured or killed by medication errors each year; seniors most at risk due to the polypharmacy risk factor. Adding pharmaceutical counseling to patients on four or more medications decreases the risk of medication errors
Read More →
Pressure Ulcers Management
Pressure ulcers are a major complication associated with the loss of mobility, activity, increased moisture, poor nutrition, friction, shear, and altered sensory perception. They are caused by unrelieved compression of the blood vessels and tissues resulting in the lymphatic system not filtering waste products.
Read More →
Preventing Falls in the Elderly Long Term Care Facilities
The elderly long-term care population is at increase risk for falls and fall related injuries. The implementation of a fall prevention program is important for ensuring resident safety. Systematically assessing residents’ risk for falls and implementing appropriate fall prevention interventions can reduce the number of falls in the elderly long-term care residents.
Read More →
Providing Appropriate Nursing Care for the Developmentally Disabled Child
Developmental disabilities are birth defects related to a problem with how body parts and/or body systems work. These defects may affect multiple body parts and/or systems. There are four types of disability discussed in this article including nervous system disability, sensory-related disability, metabolic disorders and degenerative disorders.
Read More →
Recognizing and Overcoming Toxic Leadership
Toxic nurse managers are detrimental to organizations, diminishing staff morale, thwarting creativity, and creating unnecessary job stress. Toxic nurse managers can also negatively affect an organization’s bottom line as staff absenteeism may increase, job satisfaction and critical thinking may decrease, leading to turnover and complicating innovation, decision making, and problem solving.
Read More →
Relationships among the Elderly: The Effects on One's Health and Psychosocial Well Being
Advances in medicine are allowing many adults to live longer lives than previous generations. In fact, the elderly population is becoming one of the largest growing sectors of the present population. Recently, researchers have begun studying what factors contribute to successful aging. These studies are showing that the impact of family and social relationships plays an important part in one’s health and psychosocial well being. People can get lonely, so dating for seniors could be a great boost for their psychological well being.
Read More →
Russian Nurses after the Crimean War
As it is well known, the Crimean War (1854-1856) marked the turning point in the history of nursing. The outstandingly self-sacrificing work of Florence Nightingale and 38 British nurses, who worked day and night in Turkish hospitals, providing help and necessary care to the sick and wounded soldiers, was highly praised and acknowledged in Britain. Their hard labor and efficient management in improving sanitary conditions in the army hospitals brought about a new approach to women’s participation in hospital care.
Read More →
Sisters of Mercy in Prisons
Evolution of prisons in European countries has mainly been highlighted by the specialists on law and social studies, while participation of nurses in developing the up-to-date system of treating people sentenced by the societies to spend a part of their lives in jails still remains in a shadow. This survey is an attempt to take a brief glimpse of the contribution of sisters of mercy, members of the first European communes of nurses, to creating adequate conditions for prisoners and changing public's attitude towards rehabilitation of criminals and their possible return to normal life in the society.
Read More →
Smoking Cessation Education in the Elderly
The role of the professional nurse as direct care provider and educator is pivitol in providing clients with the information and support necessary to facilitate smoking cessation and improve client health outcomes.
Read More →
The Algorithm of Rapid Response (RRT Nursing)
Carrying the beeper for a shift as a member of a rapid response team entails being ready at a moment’s notice to respond to the call for help from a nurse or family member concerned about a patient change of condition, no matter how subtle or seemingly inconsequential the clinical change may be.
Read More →
The Importance of Communication and Education toward Patient Literacy: The Relationship of Functional Health and Patient's Knowledge of Their Chronic Disease and Metabolic Disorder
The aging populations in the U.S. with ‘Essential’ Hypertension are showing inadequate health literacy, plus its impact on patients with idiopathic chronic diseases such as type II, adult onset Diabetes Mellitus are makeable. To identify among patients with hypertension and/or with diabetes the relationship between their functional health literacy levels, and the role of the registered nurse as communicator and educator.
Read More →
The Importance of Supporting Mothers Who Breastfeed
There are many health benefits to breastfeeding children such as lower mortality rates, ideal nutritional values, and long term benefits such as healthy weights and higher intelligence later in life. The positive aspects of breastfeeding extend to maternal health as well, such as lower rates of breast and ovarian cancers and decreased occurrences of post-partum depression.
Read More →
The Importance of Understanding Hypertension: The Role of a Registered Nurse as an Investigator
The primary care nurse owes it to themselves and their patients to be informed on the chronic diseases they manage in order to achieve maximum patient compliance and satisfaction. Well informed, confident practitioners will be able to deliver evidence-based structured advice, and in doing so reduce morbidity and mortality rates from cerebrovascular accidents and cardiovascular disease for patients regardless of age, gender, or ethnicity.
Read More →
The new meaning of the word "STAT"
The word “STAT” and what it means to me compared to what it means to others. In this instance it was sort of a “Hurry up and wait” affair.
Read More →
The Significance of the Missed Assessment: HIV/AIDS in the Older Adult
The health care system has faced many struggles related to the understanding the HIV virus and in caring for those affected and likely to be affected by this life threatening communicable disease.
Read More →
The Signs and Symptoms' of Cardiomyopathy: The Awareness and Actions of the Registered Nurse
A careful history-taking by the registered nurse or practitioner along with a complete physical examination can reveal cardiomyopathies, but it is appropriate to confirm the diagnosis with a transthoracic echocardiography and selected laboratory studies.
Read More →
There Are No Simple Cases
As a twenty year experienced recovery room nurse, I know that no case is ever the same. People are individuals. They react differently to medications. They metabolize drugs at different rates depending on age, body mass, body temperature, kidney and liver functions. Although everyone is different, I can basically expect a certain outcome in recovering people. But in saying this, you can always expect the unexpected.
Read More →
Thyroid Storm and the AACN Synergy Model
Thyroid storm, or thyrotoxic crisis is a rare, but critical hypermetabolic state requiring emergent treatment.
Read More →
To Gown or Not to Gown? For MRSA Prevention, That Is the Question.
The Center for Disease Control (CDC) states that standard precautions should be used for all patients and should be enough to prevent the spread of most MRSA cases. However, in acute-care settings the CDC recommends additional contact precautions be implemented when there are ongoing MRSA transmissions, current infections, previous colonization, and in other special circumstances.
Read More →
UN Noticed
It takes more than the knowledge of degrees can provide. It takes the UN noticed hero, our nursing assistant.
Read More →
Videos, Bells and Whistles; Fall Risk or Injury Prevention?
The term “Never Event” is not friendly. Never events consist of 28 occurrences on a list of inexcusable outcomes in a healthcare setting. They are defined as "adverse events that are serious, largely preventable, and of concern to both the public and healthcare providers for the purpose of public accountability.
Read More →
Where are the Children? Pediatrics in an integrated format
Integrating pediatric content is a challenge to nurse educators. Limited information exists regarding the most effective method of teaching pediatrics. Nurse educators disagree on placement of pediatric content. Pediatric concepts are at risk of getting lost or deemed unimportant as other concepts are expanded. This article will examine the experience of educators in a nursing program that integrated pediatric content. The benefits and disadvantage of teaching pediatrics in an integrated format will be discussed.
Read More →
Detour Off The Sepsis Road: Early Recognition is Key
At present, the US reports approximately 750,000 cases of sepsis a year and estimates 1 million cases by 2020 With a mortality rate of 30%, an estimated 250,000 annual deaths, and hospital costs exceeding $16 billion, sepsis has become a burden. It is imperative to increase the awareness and early recognition of sepsis.
Read More →
The Power of Preceptorship
The clinical experience is an essential component to nursing education. The identification of formal preceptors grows increasingly difficult as competition for clinical sites and nursing faculty shortages continue to place a strain on the system.
Read More →
Increasing New Graduate Nurse Retention from a Student Nurse Perspective
Research shows that turnover rates are high for new nurse graduates as a result of a stressful work environment coupled with inadequate support during the transition from student to professional practice. This article seeks to define the problem of new nurse graduate retention, examine strategies implemented by specific organizations that decreased turnover rates of new graduate nurses, and offer recommendations for the new graduate nurse about to enter professional practice.
Read More →
The Challenge of MSA: Multiple System Atrophy
Five months later his wife called and said “Jack has been diagnosed with MSA and there’s not much they can do.” I asked if she meant MRSA. “No, it’s like Parkinson’s but there’s no known medication that helps.” The diagnosis was made by a neurologist who specializes in multiple system atrophy (MSA).
Read More →
Jobs: Supply and Demand for Registered Nurses
A nursing shortage across America is generating a variety of preventable complications in the medical care system, which includes medication errors, overcrowding in emergency rooms, and even unexpected patient deaths.
Read More →
The Healing Impact of Palliative Care Gerontology
Palliative care is a philosophy and treatment to give an improved quality of life to those near the end of life and those with life-limiting conditions.
Read More →
Examining the Transition for New Graduate Professional RN
Transition into the role of the professional nurse is cause for great excitement and apprehension for the student nurse. As a soon to be BSN graduate, this author noted a similar theme amongst classmates which provided an opportunity for inquiry to highlight key strategies for successful transition for the entry-level professional nurse
Read More →
Are New Graduate Nurses Being Taught About the Importance of Nursing Rounds?
This study helps to determine if new graduate nurses have any knowledge about nursing rounds and if they are using nursing rounds as a way to organize their practice.
Read More →
Risperdal and Autism
Autism is a developmental disorder in children and continues through adulthood. Currently, there is no known cause or cure for autism. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the use of Risperdal for the treatment of aggressive behavior in autistic patients ages 5-16 years old.
Read More →
Female R.N.'s: You May Be Working for Less Pay than Your Male Counterparts
Although CRNP’s and PA’s are comparable at the most basic of levels, more is expected of CRNP’s because we are licensed to do more! What we cannot do is work a 50 hour week for a 40 hour paycheck! So why do we continue to the right thing for less pay?
Read More →
Can I Depend On You?
An LPN Instructor at East Central Technical College in Douglas, Georgia requires an experience for her nursing students.
Read More →
End-Of-Life-Care: Are Nurses Educationally Prepared?
End Of Life Care study in the RN Journal. Are nurses prepared to offer quality end-of-life care to patients and families?
Read More →
Nursing Students Readying to Save Lives
Recognizing the findings in a patient with an impending myocardial infarction (MI) and intervening appropriately is essential for healthcare providers in improving patient outcomes.
Read More →
Caring and the Professional Practice of Nursing
Leininger’s Theory of cultural care and Jean Watson’s Theory of human caring in the RN Journal.
Read More →
The Crisis in Iraq
The impending military conflict in Iraq will significantly affect the current capacities of the Iraqi health system. The health system in Iraq has undergone incredible stressors during the past two decades. Health professionals can better connect with their Iraqi colleagues through understanding the specific context of the upcoming crisis. Drawing from several sources, including first hand accounts from six Iraq visits in the last five years and consulting for several NGOs and UN organizations, this article provides a brief introduction to the Iraqi context, highlighting both the strengths and needs of the Iraqi health system.
Read More →
Help Me Get Better
A Registered Nurse reflects on her experiences as an RN professional!
Read More →Get Published for Free
Browse by Tag
advocate aging anesthesia behavior cardiac care Case Study child children clinical compassion COVID-19 critical care death diabetes disease education emergency department end of life ethical principles ethical values ethics future of nursing health health care ICU medication mental health nurse Nurse Education nursing nursing education nursing ethics nursing faculty nursing school nursing students PACU patient care patient outcomes patient safety pediatric poem profession risk factors stress student nurse students teaching therapy treatment
Most Popular Last Month
More from RN Journal
Nurse Camp: Planting Nursing Seeds in High School
Lung Cancer: A Case Study
Nurse, please pray with me.
A Competent Psychiatric Nurse: What role does empathy provide in competency?
Impact of Stress and Lifestyle on Cardiac Health in College Students
Medical Equipment
Navigating Nursing School: Do's and Don'ts for Aspiring Nurses
Applying Current Standards of Wound Care Practice: Improve Patient Outcomes and Save Precious Time
Are Canadian Nurse Practitioners here to stay?












